Imagine a bustling marketplace, brimming with vendors selling everything from apples to automobiles. Each vendor has a different size, representing the value of their products and their influence within the market. This, in essence, is how a market capitalization weighted index works. Just like a large vendor commands more attention and sway in the marketplace, companies with larger market capitalizations hold greater weight in these indices, influencing the overall market direction.

Image: 365financialanalyst.com
These indices are not theoretical concepts; they are the backbone of many investment strategies. They offer investors a way to track the performance of a specific market segment or a broader economy. Think of them as a snapshot, capturing the health and direction of the investment world at a given point in time. Understanding market capitalization weighted indices is crucial for any investor seeking to make informed decisions and navigate the dynamic world of finance.
Understanding the Mechanics of Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
What are Market Capitalization Weighted Indices?
Market capitalization weighted indices are constructed based on the total market value of each company listed in the index. This market capitalization, often termed “market cap,” is calculated by multiplying the company’s outstanding shares by its current stock price.
For instance, a company with 10 million shares outstanding trading at $50 per share has a market cap of $500 million. In a market capitalization weighted index, this company would have a larger weighting compared to a company with a market cap of $100 million. The larger the market cap, the more influence it exerts on the index’s overall performance.
The History and Significance of Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
The concept of market capitalization weighted indices dates back to the early 20th century. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), arguably the most famous stock market index, was initially a price-weighted index. However, the advent of computers and automated trading systems made it easier to calculate market capitalization weighted indices, leading to their widespread adoption.
Today, these indices are the dominant force in global stock markets. The S&P 500, Nasdaq Composite, and FTSE 100 are all prime examples of market capitalization weighted indices that are tracked globally. Their significance lies in their ability to provide investors with a reliable gauge of market performance, mirroring the collective sentiment and the direction of large-cap companies.
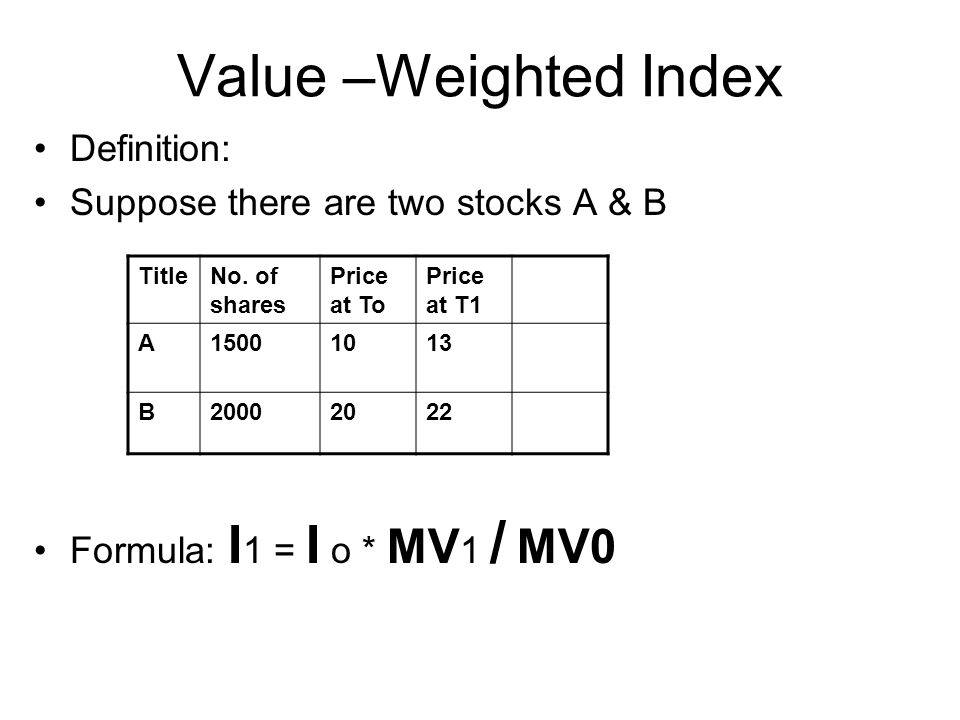
Image: necteo.com
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
Market capitalization weighted indices offer several advantages, including:
- Comprehensive Representation: They encompass a wide range of companies within a specific market segment, providing a broad view of market performance.
- Transparent and Objective: The weighting methodology is straightforward and quantifiable, eliminating subjective biases in index construction.
- Liquidity and Trading Efficiency: Larger companies tend to have more liquid shares, facilitating efficient trading and reducing price volatility.
However, these indices also come with some drawbacks:
- Bias towards Large-Cap Companies: They may overemphasize the performance of large-cap companies, potentially underrepresenting the growth potential of smaller companies.
- Vulnerability to Market Bubbles: In a market bubble, the inflated valuations of large-cap companies can distort the index’s performance, creating a false sense of market strength.
- Limited Diversification: While encompassing a broad range of companies, these indices may lack the diversity offered by other indices, potentially increasing investment risk.
The Evolving Landscape of Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
Investors are becoming increasingly aware of the shortcomings of traditional market capitalization weighted indices. As a result, there’s a growing interest in exploring alternative index methodologies, such as equal-weighted indices or fundamental-weighted indices.
Equal-weighted indices assign equal weight to each company within the index, regardless of its market capitalization. This approach offers greater diversification and reduces the bias towards large-cap companies. Fundamental-weighted indices use financial metrics like earnings, dividends, and book value to determine company weightings, providing a more nuanced representation of company performance than market capitalization alone.
These evolving trends reflect a growing demand for more balanced and representative index methodologies. As investment strategies evolve, investors are seeking indices that provide a more nuanced perspective on market performance and offer greater investment opportunities.
Tips for Investors Utilizing Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
Market capitalization weighted indices are valuable tools for investors, but effective utilization requires mindful consideration and a balanced approach.
- Understand Index Construction: Delve into the methodology behind the index, ensuring you comprehend the factors determining company weightings to make informed decisions.
- Assess Market Conditions: Be aware of market dynamics, recognizing the potential impact of large-cap company performance on the overall market and index performance.
- Consider Diversification: Explore other investment strategies and index methodologies to diversify your portfolio and reduce investment risk, particularly during market volatility.
While market capitalization weighted indices offer valuable insights into market performance, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations and adopt a balanced investment approach. By diversifying your strategies, understanding the market context, and critically evaluating index methodologies, you can leverage the power of these indices while mitigating potential risks.
FAQs about Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
Q: What is the difference between a market capitalization weighted and a price-weighted index?
A: A market capitalization weighted index uses the total market value of each company to determine its weight, while a price-weighted index assigns weight based on each company’s stock price. Price-weighted indices tend to give more weight to high-priced companies, while market capitalization weighted indices reflect the overall market value of each company.
Q: How are market capitalization weighted indices used in asset allocation?
A: Investors employ these indices as benchmarks for their portfolios, aiming to match or exceed the index performance. They also use them to track specific market sectors, allocating assets accordingly.
Q: Are market capitalization weighted indices always the best option for investors?
A: Not necessarily. While they offer broad market exposure, their bias towards large-cap companies may not be suitable for all investors, particularly those seeking smaller-cap growth opportunities. Considering alternative index methodologies, like equal-weighted or fundamental-weighted indices, can provide a more diversified approach.
Market Capitalization Weighted Indices
https://youtube.com/watch?v=g6diE71GdpI
Conclusion
Market capitalization weighted indices stand as a cornerstone of the global financial landscape, providing investors with a valuable window into the collective performance of large-cap companies. They offer transparency, efficiency, and broad market representation, yet it’s vital to acknowledge their limitations and explore alternative index methodologies for a more diversified and balanced investment approach.
Are you interested in learning more about the evolving world of index methodologies and diversifying your investment strategies? Let us know your thoughts and questions in the comments below.