In the realm of global finance, the foreign exchange (forex) market stands as the largest and most liquid marketplace, an arena where currencies of nations are bought, sold, and traded 24 hours a day, five days a week. The participants in this vast network range from colossal institutional investors and multinational corporations to intrepid individual traders, all seeking to capitalize on the fluctuations in currency exchange rates.

Image: forexrobotonline1.blogspot.com
For those unfamiliar with this fascinating domain, understanding the ins and outs of buying and selling forex is paramount. In this exhaustive guide, we embark on a journey to demystify the forex market, deciphering its complexities and equipping you with the knowledge necessary to navigate this dynamic landscape.
Defining Forex Trading
Forex trading, also known as currency trading, involves the simultaneous purchase of one currency while selling another. The aim of this trade is to profit from the difference in exchange rates, which fluctuate constantly due to a multitude of factors. These factors include economic data, political events, interest rate decisions by central banks, and global market sentiment.
Benefits of Forex Trading
The forex market offers a plethora of advantages to its participants. Here are some notable benefits:
- High Liquidity: Forex is the world’s most liquid market, boasting an average daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. This liquidity facilitates effortless execution of trades without significant price slippage.
- 24/5 Accessibility: Unlike traditional stock markets, the forex market operates continuously, 24 hours a day, five days a week. This around-the-clock availability allows traders to respond to market movements and seize opportunities at any time.
- Low Transaction Costs: Forex brokers typically charge minimal spreads and commissions, making it an alluring option for cost-conscious traders seeking to maximize their profits.
- Leverage: Many forex brokers provide traders with access to leverage, allowing them to control a larger position size than their account balance. This leverage can amplify potential profits but also magnifies potential losses.
Understanding Currency Pairs
Currencies are always traded in pairs in the forex market. Each pair consists of a base currency (the first currency listed) and a quote currency (the second currency listed). For instance, the EUR/USD currency pair represents the euro as the base currency and the US dollar as the quote currency. The exchange rate for this pair indicates how many US dollars are required to purchase one euro.
Currency pairs are further classified into three main categories:
- Major Pairs: These are the most commonly traded currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. They are characterized by high liquidity and relatively low spreads.
- Minor Pairs: Composed of currencies from smaller economies, minor pairs offer greater volatility and potentially higher returns but also come with increased risk.
- Exotic Pairs: These pairs involve currencies from emerging or developing economies. Exotic pairs are less liquid and more volatile, requiring a higher risk appetite.
How to Buy and Sell Forex
Traditionally, forex trading was conducted over-the-counter (OTC), requiring traders to contact a bank or brokerage firm to execute their orders. However, the advent of online trading platforms has revolutionized the process, making it more accessible to individual traders.
To begin buying and selling forex online, you need to:
- Choose a Forex Broker: Select a reputable and regulated forex broker that offers a user-friendly trading platform, competitive spreads, and reliable customer support.
- Open a Forex Trading Account: Fund your trading account with the initial capital you are willing to risk. It’s crucial to remember that forex trading involves risk, and you should never invest more than you can afford to lose.
- Analyze Market Conditions: Utilize technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify potential trading opportunities. Monitor economic data, news events, and central bank announcements that may influence currency exchange rates.
- Place an Order: Once you have identified a trading opportunity, place an order to buy or sell a specific currency pair. Specify the order size and type (market order, limit order, or stop order).
- Manage Your Risk: Implement sound risk management strategies, such as using stop-loss orders and controlling your leverage. It’s crucial to limit your losses and protect your capital.
Strategies for Forex Trading
There are numerous forex trading strategies available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some popular strategies include:
- Scalping: A short-term trading strategy that aims to profit from small price movements over a short period of time.
- Day Trading: Involves buying and selling currencies within the same trading day, typically closing all positions before the end of the day.
- Swing Trading: A medium-term trading strategy that holds positions for several days to several weeks, aiming to capture larger price swings.
- Trend Trading: Focuses on identifying and trading within established trends, buying currencies that are trending upwards and selling those trending downwards.
- Carry Trading: A strategy that involves borrowing a currency with a low interest rate to purchase a currency with a higher interest rate, profiting from the interest rate differential.
Conclusion
Navigating the foreign exchange market demands a thorough understanding of its workings, along with a comprehensive grasp of currency pairs, trading strategies, and risk management techniques. While the forex market presents a multitude of opportunities for skilled traders, it is imperative to exercise caution and approach trading with a well-informed and disciplined mindset. Those who venture into this realm with knowledge and prudence stand a better chance of harnessing its potential and reaping its rewards.
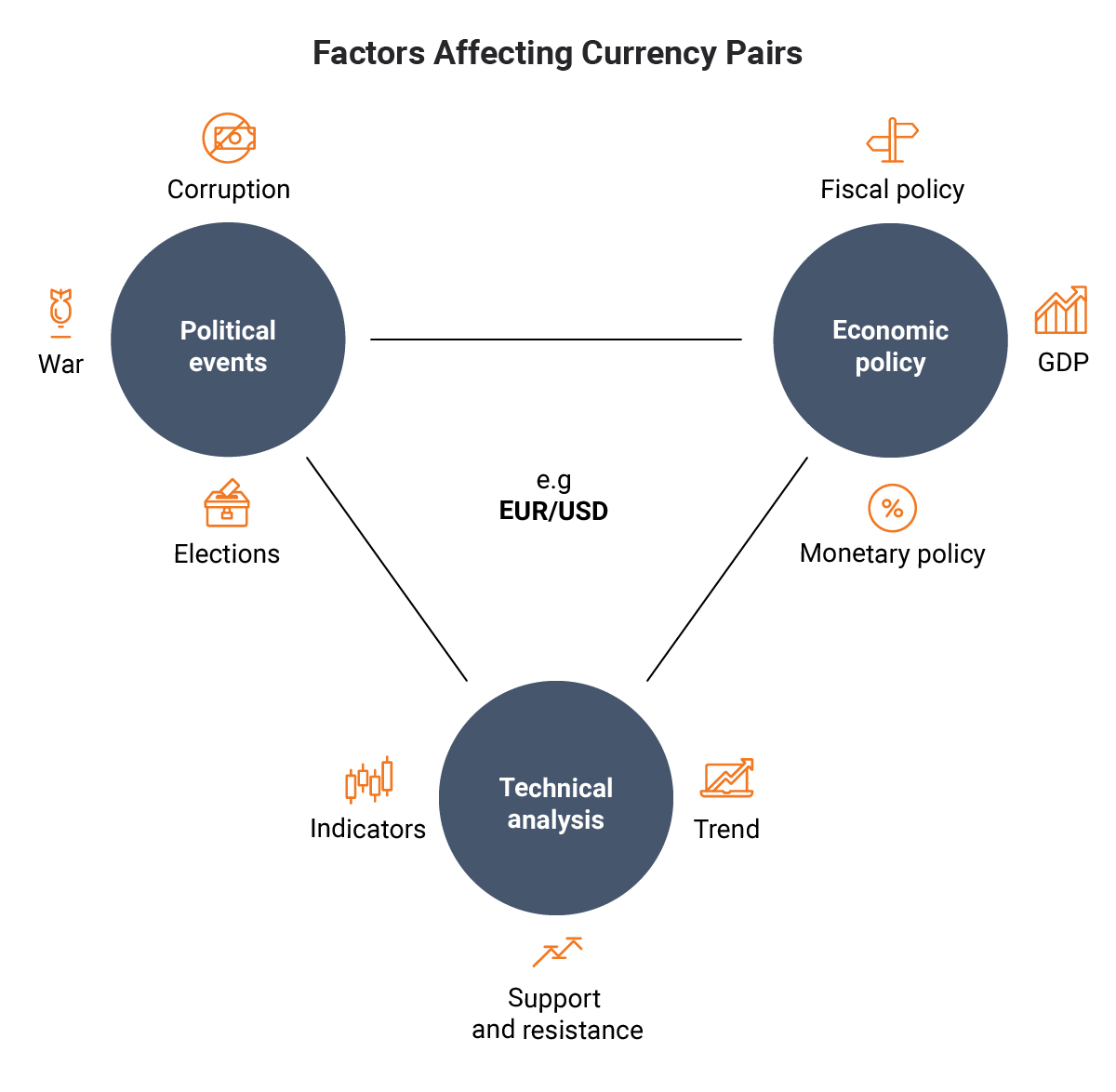
Image: www.dailyfx.com
Buy And Sell Forex Meaning






