India’s economic landscape presents a dichotomy that demands careful analysis: a substantial current account deficit coupled with robust foreign exchange reserves. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for grasping the challenges and opportunities facing India’s economy.

Image: www.cnbctv18.com
Delving into Current Account Deficit: A Balancing Act
In essence, a current account deficit arises when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, coupled with net outflows on investment income and transfers. India’s current account deficit has been a persistent concern, reflecting a wider gap between its imports and exports. This gap is largely attributable to the nation’s reliance on energy imports, particularly crude oil. Moreover, India’s appetite for consumer goods and advanced equipment has further exacerbated the deficit.
The immediate impact of a current account deficit is a reduction in the country’s foreign exchange reserves. However, India’s paradox lies in its high forex reserves, buoyed by robust inward remittances from overseas Indians and increased foreign investment. This seemingly contradictory situation warrants closer examination.
Exploring the Paradox: External Factors at Play
India’s foreign exchange reserves have reached unprecedented levels, surpassing $600 billion, reflecting several external factors. A key contributor is the robust inflow of remittances, with Indians working abroad sending substantial sums back home. These remittances serve as a valuable source of foreign exchange, mitigating the impact of the current account deficit to some extent.
Another factor underpinning India’s forex reserves is the surge in foreign direct investment (FDI). International investors are drawn to India’s growth potential and the government’s efforts to improve the business environment. This influx of FDI further strengthens India’s foreign exchange position.
Policy Imperatives: Striking the Right Balance
While the high forex reserves provide a cushion against short-term financial shocks, they do not negate the need to address the underlying issue of the current account deficit. Policymakers must strike a delicate balance between managing the deficit and maintaining economic growth.
หนึ่ง The primary focus should be on enhancing exports by promoting manufacturing and creating a globally competitive business environment. This will help narrow the trade deficit and reduce reliance on imports.
Two India must also explore ways to reduce its energy dependence through renewable energy sources and other alternatives. This will not only ease the pressure on the current account but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Three It is imperative to attract and retain foreign investors by continuing to improve the business climate and providing a stable policy environment. This will sustain the flow of FDI, further bolstering foreign exchange reserves.
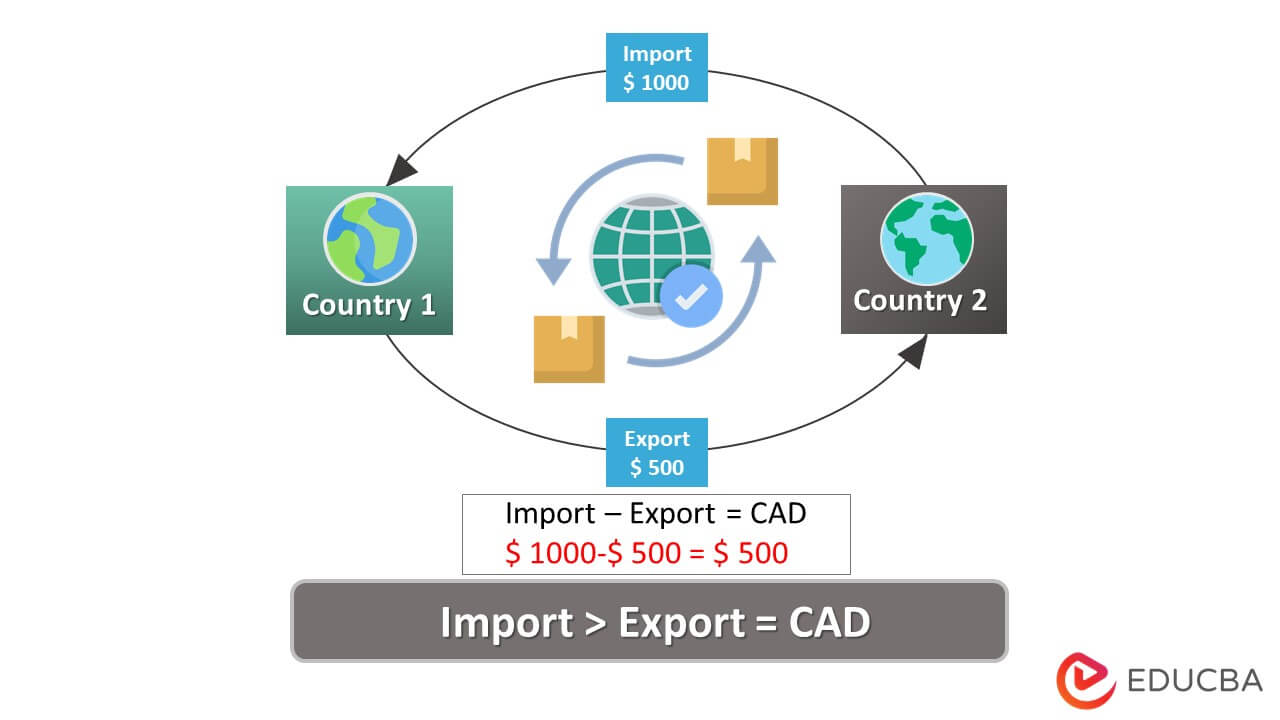
Image: www.educba.com
India Is Having Current Account Deficit And High Forex Reserve
Conclusion: A Path to Sustainable Growth
India’s current account deficit and high forex reserves present a complex economic landscape. While the robust forex reserves provide a safety net, the underlying deficit cannot be ignored. To achieve sustainable growth, policymakers must implement a comprehensive strategy that fosters exports, reduces energy dependence, boosts FDI, and encourages domestic manufacturing. Balancing these imperatives will be critical in charting a stable and prosperous economic future for India.






