Introduction
India’s foreign exchange reserves play a pivotal role in safeguarding the nation’s economic stability and mitigating external shocks. Over the years, the country has consistently maintained a substantial stockpile of foreign currency, which acts as a buffer against unforeseen circumstances like global economic turmoil, currency depreciation, or geopolitical tensions. This article delves into the significance of India’s forex reserves, examining their composition, management, and impact on the Indian economy.
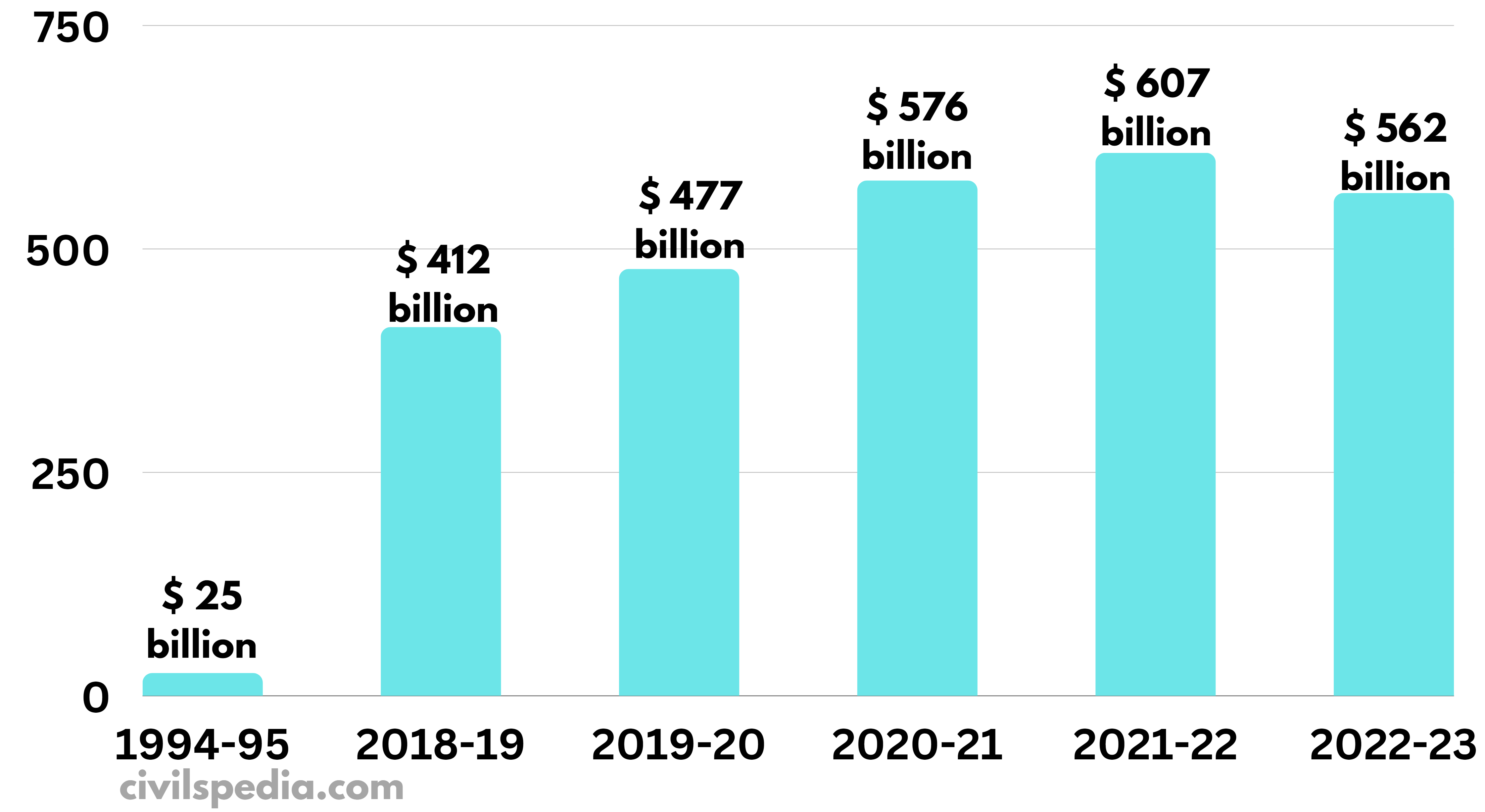
Image: civilspedia.com
Understanding Forex Reserves
Foreign exchange reserves, often referred to as forex reserves, comprise the total amount of foreign currency, gold, and other liquid assets held by India’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These reserves accumulate primarily through trade surpluses, foreign direct investments, inward remittances, and inflows from extraordinary financial sources. Forex reserves serve as a crucial tool for managing the volatility in the value of the Indian rupee against other currencies, ensuring economic resilience and protecting against external financial risks.
Composition of India’s Forex Reserves
India’s forex reserves are diversified across various asset classes to minimize risk and optimize returns. Currency assets, comprising approximately 60% of the reserves, dominate the portfolio. These include major global currencies like the US dollar, the euro, the British pound, and the Japanese yen. Gold makes up about a quarter of the reserves, providing a hedge against currency fluctuations and geopolitical risks. Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), an international reserve asset allocated by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and reserve positions in the IMF account for the rest of the reserves.
Management of Forex Reserves
The RBI bears the responsibility of managing India’s forex reserves. The bank employs a prudent investment strategy, prioritizing capital preservation and liquidity. Forex reserves are invested in foreign government securities, corporate bonds, and supranational institutions that offer a favorable risk-return profile. RBI closely monitors global economic conditions, market trends, and geopolitical developments to adjust its investment strategies and maintain an adequate level of reserves.
Image: bestsystemforexwinners.blogspot.com
Benefits of Ample Forex Reserves
Maintaining robust forex reserves offers numerous advantages to the Indian economy:
-
Currency Stability: Forex reserves provide a buffer to mitigate external shocks that might impact the Indian rupee’s value. By intervening in the foreign exchange market, RBI can stabilize the rupee, curtailing volatility and safeguarding the nation’s import capacity.
-
Trade Facilitation: Ample forex reserves ensure seamless trade transactions, enabling timely import payments and minimizing the risks associated with currency fluctuations. This facilitates international commerce and promotes economic growth.
-
External Debt Management: Forex reserves serve as a cushion to meet external debt obligations, mitigating the risk of default and boosting the country’s creditworthiness in international markets.
-
Investor Confidence: Ample forex reserves instill confidence among global investors, signaling the country’s resilience and its ability to withstand financial shocks. This привлекает foreign investment, which further strengthens the economy.
What Is Present Forex Reserve Of India
Conclusion
India’s forex reserves are a vital lifeline for safeguarding the nation’s economic sovereignty and mitigating vulnerabilities to global economic downturns. The prudent management of these reserves by the RBI ensures stability in the foreign exchange market, promotes trade and economic growth, and bolsters investor confidence. As the Indian economy continues to grow and integrate with global markets, the significance of maintaining robust forex reserves will only increase. By nurturing this precious financial asset, India secures its economic future amidst the vagaries of the global economic landscape.






