In the dynamic landscape of global finance, the foreign exchange (forex) market stands as a behemoth, facilitating the exchange of currencies between nations. Within this labyrinthine system, numerous types of transactions play vital roles, shaping the ebb and flow of currencies and influencing countless lives worldwide.
Image: www.fxpremiere.com
From humble beginnings to its present-day dominance, the forex market has evolved as a lifeline for international trade, investment, and travel. At its core, the exchange of currencies allows individuals and businesses to transact seamlessly across borders, bridging economic gaps and connecting the world in unprecedented ways.
Spot Transactions: A Glimpse into the Present
Spot transactions, the most prevalent form of forex trading, involve the immediate exchange of currencies at an agreed-upon rate, also known as the spot rate. These transactions are typically settled within two business days, providing a convenient and timely way to meet immediate financial obligations.
Forward Transactions: A Window into the Future
In contrast to spot transactions, forward transactions cater to longer-term currency needs. Buyers and sellers agree upon a price for a set amount of currency to be exchanged on a predetermined future date. Forward contracts offer a way to hedge against potential fluctuations in currency values, ensuring greater certainty in future financial dealings.
Swap Transactions: The Art of Currency Exchange and Interest Rate Management
Swap transactions represent a sophisticated form of forex exchange that encompasses both spot and forward components. Typically involving two currencies with varying interest rates, swap deals allow parties to simultaneously exchange principal amounts and swap interest payments at agreed-upon rates. These complex transactions are often used by governments, banks, and large corporations to manage currency risks and optimize interest rate strategies.
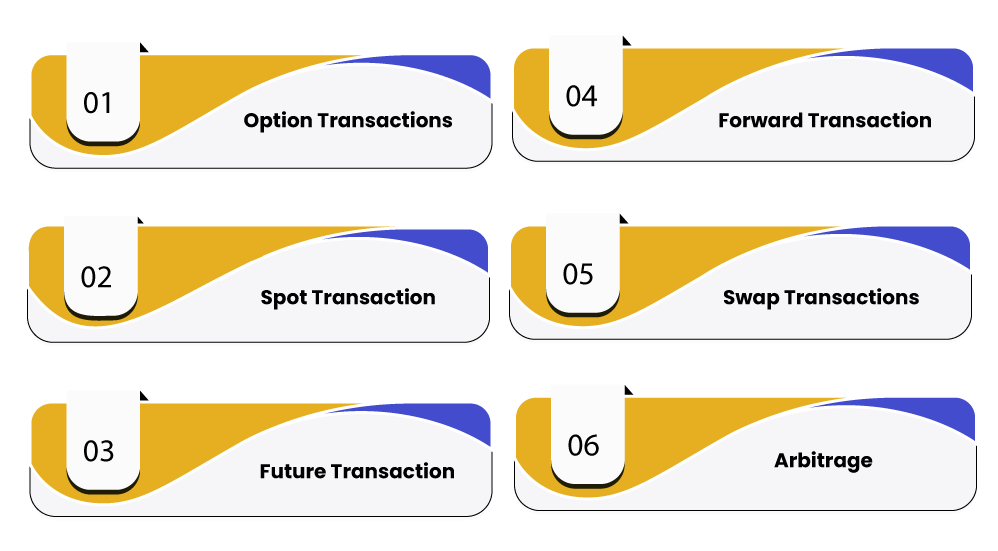
Image: swaritadvisors.com
Option Transactions: Navigating the Waters of Risk
Forex options provide a flexible instrument for managing currency risks without the obligation to execute a trade. These contracts offer the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price and expiration date. Options allow traders to speculate on future currency movements or hedge against unfavorable exchange rate fluctuations.
The Symphony of Hedging: Safeguarding Against Currency Volatilities
Hedging stands as an essential component of forex transactions, empowering individuals and businesses to mitigate currency-related risks. Through hedging, traders can effectively neutralize potential losses arising from unfavorable exchange rate fluctuations. Forex options play a critical role in hedging strategies, providing a safety net to navigate the often-volatile waters of currency markets.
Currency Swaps: A Tapestry of Borrowing and Currencies
Currency swaps, similar to traditional swap transactions, involve the exchange of principal amounts in two different currencies. However, these swaps encompass an additional layer of complexity, as they also include periodic interest payments based on predetermined rates and maturities. Currency swaps serve as essential tools for corporates and governments seeking to manage currency exposures and optimize borrowing costs.
Types Of Transaction In Forex Market
Conclusion
The vast expanse of the forex market presents an intricate tapestry of transactions, each playing a vital role in the global flow of currencies. Spot transactions facilitate immediate exchanges, forward transactions offer certainty in future dealings, swap transactions cater to complex currency and interest rate management, option transactions provide risk management flexibility, hedging safeguards against currency volatility, and currency swaps enable optimal borrowing strategies. Understanding the nuances of these transactions unlocks the gateway to navigating the global finance landscape with greater confidence and success.






