Imagine yourself on a global stage, where currency values fluctuate like stock prices, and fortunes are made and lost in the blink of an eye. Welcome to the thrilling world of forex trading, where the exchange rates between different countries’ currencies are the trading commodities. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamental concepts and provide practical insights to empower even novice traders with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic market.
Image: forextraininggroup.com
What is Forex Trading?
Forex, short for foreign exchange, refers to the trading of currencies. Unlike stocks or commodities, currencies are not physical assets; they represent the value of one country’s money relative to another. For instance, if the Euro (EUR) is worth 1.20 US Dollars (USD), it means that one Euro can be exchanged for 1.20 US Dollars. Forex trading involves speculating on the fluctuation of these exchange rates, aiming to profit from price movements.
The Appeal of Forex Trading
Forex trading has become increasingly popular due to several compelling advantages:
- High Liquidity: Forex is the most liquid financial market globally, with daily trading volumes exceeding $5 trillion. This liquidity ensures that traders can enter and exit positions quickly and easily without facing significant slippage.
- 24/5 Market: Forex trading operates around the clock Monday through Friday, except for weekends. This flexibility allows traders from different time zones to participate at their convenience.
- Leverage: Forex brokers offer high leverage, which can amplify both gains and losses. Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with less capital, but it also carries significant risk.
- Wide Range of Currency Pairs: Forex trading offers a diverse selection of currency pairs, including major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY, as well as minor pairs and exotic pairs. This variety caters to different trading strategies and risk tolerances.
Essential Concepts for Forex Trading
To grasp the intricacies of forex trading, it’s crucial to understand a few key concepts:
- Currency Pairs: Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. Currency pairs are denoted in the format “base currency/quote currency.” In the EUR/USD pair, the Euro is the base currency, and the US Dollar is the quote currency.
- Bid and Ask Prices: The bid price is the price at which a trader can sell a currency pair to the market, and the ask price is the price at which a trader can buy a currency pair. The difference between the bid and ask prices is known as the spread, which represents the broker’s commission.
- Pips: Pips, short for “point in percentage,” are the smallest unit of measurement for currency prices. For most currency pairs, one pip is equal to 0.0001, while for Yen-based currency pairs, one pip is equal to 0.01.
- Lot Size: A lot represents a specific quantity of the base currency in a currency pair. The standard lot size is 100,000 units, but mini lots of 10,000 units and micro lots of 1,000 units are also available.
- Margin: Margin is the amount of capital required to maintain open forex positions. Forex brokers typically require traders to maintain a certain margin level to cover potential losses.
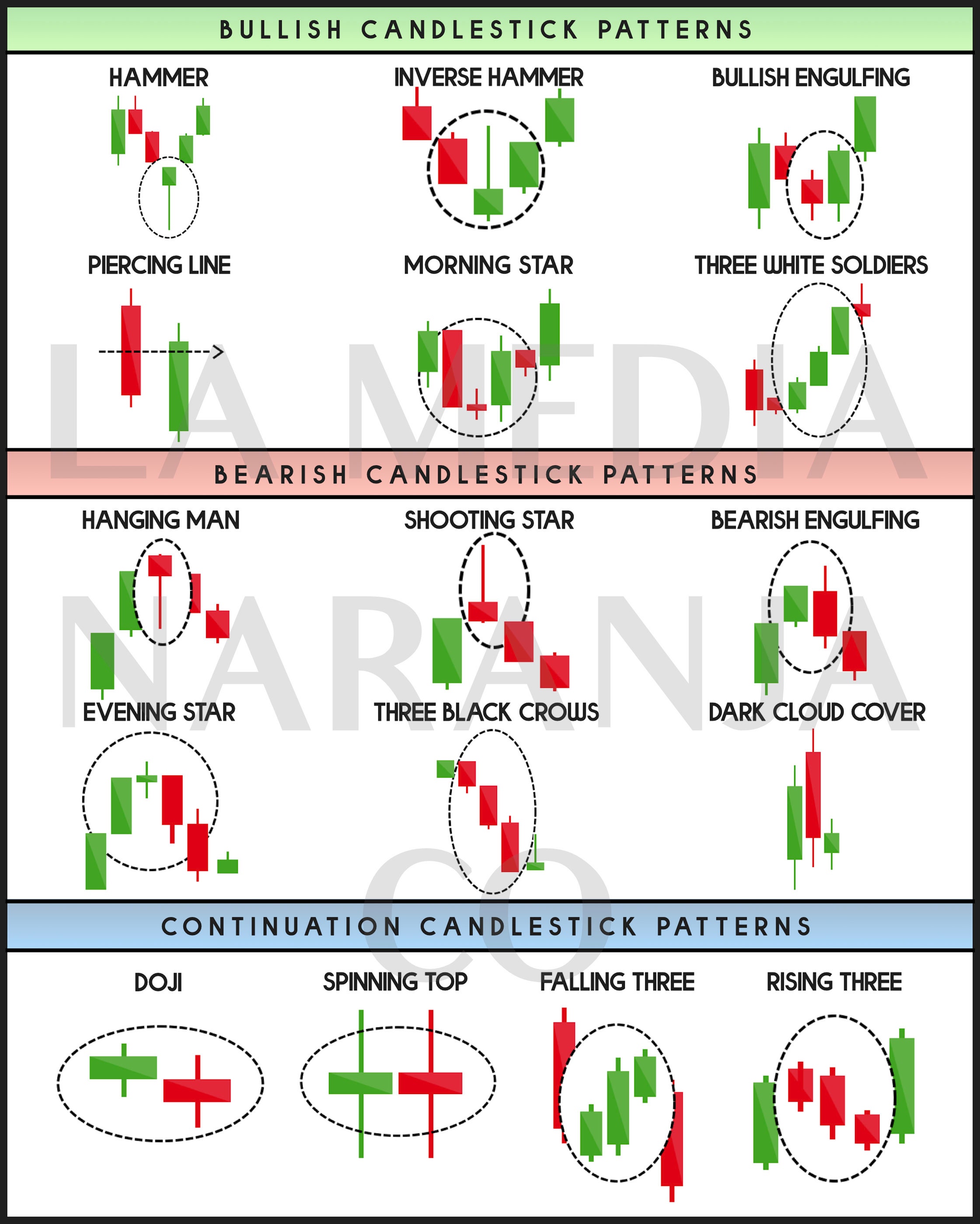
Image: www.etsy.com
Trading Strategies for Forex
Diverse trading strategies can be employed in forex trading, catering to different risk appetites and time horizons:
- Scalping: Scalping involves placing multiple small trades within a short period, profiting from small price movements. This strategy requires quick execution and tight risk management.
- Day Trading: Day trading involves opening and closing trades within a single trading session, aiming to capitalize on intraday price fluctuations. Day traders typically use technical analysis to identify trading opportunities.
- Swing Trading: Swing trading involves holding trades for a few days or weeks, following price swings and market trends. Swing traders often combine technical and fundamental analysis to make informed decisions.
- Position Trading: Position trading entails holding trades for months or even years, profiting from longer-term market trends. Position traders rely heavily on fundamental analysis and macroeconomic factors.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Forex trading carries inherent risks, making proper risk management crucial:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders automatically close a trade when a specified price is reached, limiting potential losses.
- Manage Leverage Cautiously: Leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Use leverage prudently and only trade with capital that you can afford to lose.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your trades across different currency pairs to minimize exposure to any single currency or market condition.
- Control Your Emotions: Forex trading can evoke intense emotions. Stay disciplined, avoid impulsive decisions, and don’t let fear or greed influence your trading.
- Continuous Learning: The forex market is constantly evolving. Stay informed about economic and political events, and enhance your trading knowledge through ongoing education.
Basic Knowledge Of Forex Trading
Conclusion
Embarking on the journey of forex trading requires a comprehensive understanding of its fundamentals, trading strategies, and risk management principles. By thoroughly grasping these concepts and continuously seeking knowledge, aspiring traders can navigate the forex market with greater confidence in their journey to financial success






