The VIX, or CBOE Volatility Index, is a measure of expected volatility in the stock market. It is calculated from the prices of S&P 500 index options and represents the market’s expectation of the 30-day volatility of the S&P 500 index. The VIX is often referred to as the “fear gauge” because it tends to rise when investors are fearful and expect volatility, and fall when investors are complacent and expect stability.
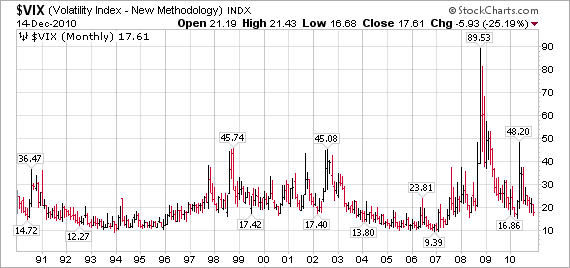
Image: seekingalpha.com
The VIX has been in a steady decline since February 2022, reaching its lowest level ever in early 2023. This has surprised many market observers, who had expected volatility to remain elevated in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and the geopolitical uncertainty surrounding the war in Ukraine.
There are a few factors that may have contributed to the low VIX. One is the strong performance of the stock market in 2022 and early 2023. When the stock market is rising, investors tend to be more complacent and less fearful of volatility. Another factor is the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes. Higher interest rates can make it more expensive for investors to borrow money, which can lead to lower volatility.
Whatever the reasons, the low VIX is a sign that the market is currently expecting a period of calm. However, it is important to remember that the VIX is not a perfect predictor of future volatility. The stock market can be volatile, and even the lowest VIX does not guarantee that there will not be another large market correction.
Historical Trends in the VIX
The VIX was created in 1993, and its history can be divided into two distinct periods: the pre-crisis period (1993-2007) and the post-crisis period (2008-present). During the pre-crisis period, the VIX was typically below 20. However, during the post-crisis period, the VIX has been much more volatile, frequently rising above 20 and even reaching 80 during the financial crisis of 2008.
The high VIX during the post-crisis period is likely due to a number of factors, including the increased uncertainty in the global economy, the rise of algorithmic trading, and the increased use of volatility-linked products by investors.
The Impact of the VIX on the Stock Market
The VIX has a significant impact on the stock market. When the VIX is high, investors tend to sell stocks and move into less risky assets, such as bonds. This can lead to a decrease in stock prices. Conversely, when the VIX is low, investors tend to buy stocks and move out of less risky assets, which can lead to an increase in stock prices.
The VIX can also affect the volatility of the stock market. When the VIX is high, the stock market tends to be more volatile. This is because investors are more fearful and are more likely to sell stocks in response to negative news. Conversely, when the VIX is low, the stock market tends to be less volatile, as investors are more complacent and are less likely to sell stocks in response to negative news.
Investing with the VIX
The VIX can be a useful tool for investors. By understanding how the VIX works, investors can make more informed decisions about when to buy and sell stocks. For example, investors may want to consider buying stocks when the VIX is low and selling stocks when the VIX is high.
There are also a number of investment products that are linked to the VIX. These products can be used to hedge against volatility or to speculate on the direction of the VIX. However, it is important to remember that investing in volatility products can be risky.

Image: variety.com
Lowest Vix Ever
Conclusion
The VIX is a complex financial instrument that can have a significant impact on the stock market. By understanding how the VIX is calculated and how it affects the stock market, investors can make more informed decisions about when to buy and sell stocks.