Have you ever dreamt of making a quick buck from the ups and downs of the financial markets? The alluring promise of potential profits has drawn many to the exciting world of derivatives – financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset. But navigating the complexities of this world can be daunting, especially for novice investors. Two popular derivatives, Contracts for Difference (CFDs) and Options, often leave individuals scratching their heads, pondering which one fits their investment strategy best. This article takes you on a journey through the intricate landscapes of CFDs and options, unveiling their nuances, advantages, and potential risks, empowering you to make informed decisions.
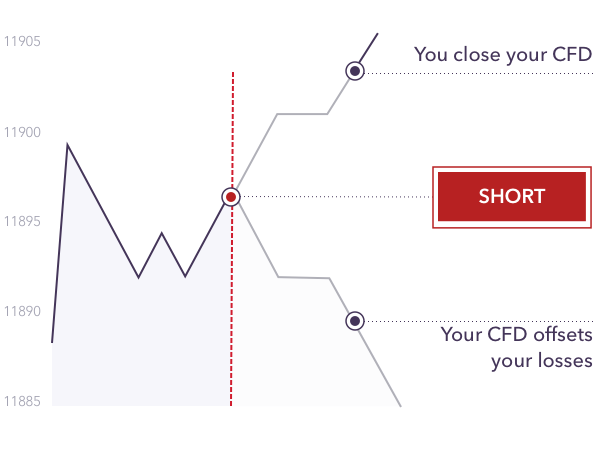
Image: www.ig.com
Both CFDs and options allow you to speculate on the future price movements of an asset without actually owning it – a concept known as “leverage.” This can be both a blessing and a curse, amplifying your potential gains but also magnifying your potential losses. Choosing between CFDs and options depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and your understanding of these instruments’ characteristics.
Understanding CFDs
What are CFDs?
Imagine a contract where you agree to exchange the difference in the price of an asset between the time you enter the contract and when you exit. That’s essentially what a CFD (Contract for Difference) is. In simpler terms, you’re betting on whether the price of an asset will go up (long position) or down (short position). You don’t actually own the underlying asset – you’re just profiting or losing the difference in price.
The Mechanics of CFDs
Let’s break down how CFDs work with an example:
- You believe the price of Apple stock will rise.
- You open a long CFD position on Apple stock at $150 per share.
- The stock price rises to $170.
- You close your position, making a profit of $20 per share (the difference between the opening and closing price).
Likewise, if the price falls to $130, you lose $20 per share. The profit or loss is calculated based on the difference in price and the number of CFD units you hold.
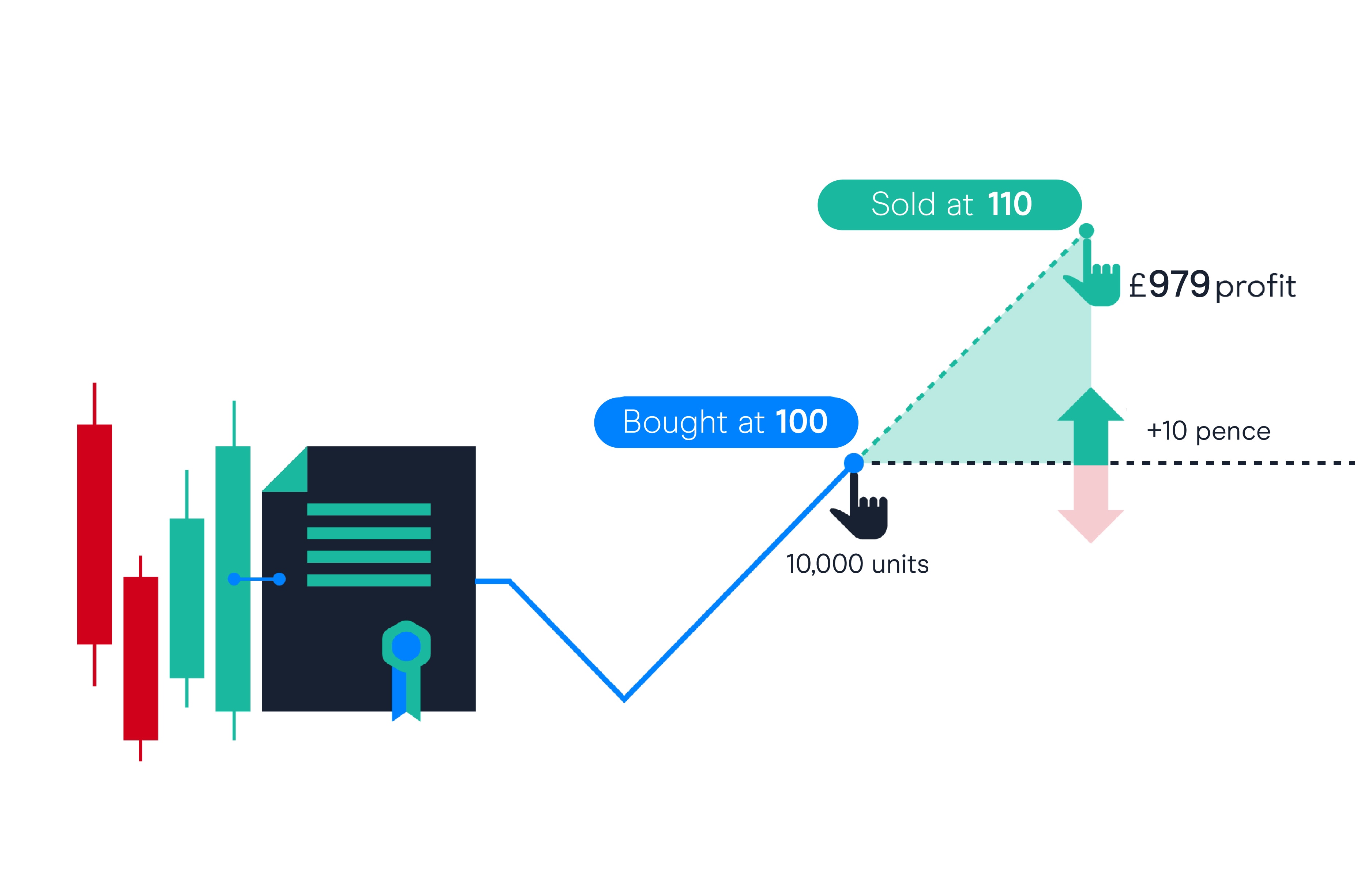
Image: www.cmcmarkets.com
Benefits of CFDs
- Leverage: This allows you to control a larger position with a smaller initial investment, potentially amplifying your profits but also your losses.
- Shorting: CFDs allow you to profit from falling prices by short-selling, which involves selling an asset you don’t own, hoping to buy it back at a lower price.
- Diversification: CFDs allow you to access a wide range of assets, including shares, indices, currencies, and commodities, diversifying your portfolio.
- Low Transaction Costs: CFD trading often involves lower transaction fees compared to traditional stock trading.
Drawbacks of CFDs
- High Risk: Leverage magnifies both gains and losses, making CFDs highly volatile and risky.
- Potential for Margin Calls: You might receive a margin call if your account balance falls below a certain level due to losses. You’ll need to deposit additional funds to maintain your position.
- Overnight Fees: Overnight holding fees can apply if you keep your CFD position open overnight, impacting your overall profitability.
- Limited Regulation: CFDs are generally less regulated than traditional financial instruments, making investor protection a concern.
Understanding Options
Options: A Deeper Dive
Options are contracts that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). Imagine it like a ticket that gives you the option to attend a concert – you can go if you want, but you’re not obligated to. Unlike CFDs, options have a fixed cost – the premium – which you pay to buy the right to exercise the option.
Types of Options
There are two main types of options:
- Call Options: Give you the right to buy an asset at a specific price. You profit when the asset price rises above the strike price.
- Put Options: Give you the right to sell an asset at a specific price. You profit when the asset price falls below the strike price.
The Mechanics of Options
Imagine you buy a call option on Apple stock with a strike price of $150 and a premium of $5 per share.
- If the price of Apple stock rises above $155 (strike price + premium), you can exercise your option, buy the stock at $150, and sell it at the market price, making a profit.
- If the stock price stays below $150, you can let the option expire worthless, losing only the premium you paid.
Benefits of Options
- Limited Risk: Your maximum loss is limited to the premium you paid for the option.
- Potential for High Returns: While potentially risky, options contracts can offer the chance for significant profits from small price movements in the underlying asset.
- Flexibility: You can adjust your options strategy based on market conditions, using strategies like “covered calls” or “protective puts” to manage your risk and potential returns.
Drawbacks of Options
- Complexity: Options trading can be complex and requires a deeper understanding of financial concepts and risk management techniques.
- Time Decay: Option premiums lose value as the expiration date approaches – a concept known as “time decay.”
- Volatility: Option prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate quickly based on market conditions, creating potential for significant losses.
CFD vs Options: Which is Right for You?
The choice between CFDs and options depends on your experience, goals, and risk tolerance.
- For beginners or those looking for simplicity, CFDs might be a better option due to their straightforward structure. However, remember the inherent risks associated with leverage.
- For experienced traders seeking more control and flexibility, options can offer a wider range of strategies and risk management tools. However, be prepared to invest time in understanding the complexities of options trading.
Key Considerations When Choosing Between CFDs and Options
Here are some crucial factors to consider when making your decision:
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you comfortable with? Consider your financial situation and investment goals.
- Trading Experience: Do you have prior experience in financial markets? CFDs might be easier for beginners, while options require a deeper understanding.
- Investment Goals: What are you hoping to achieve with your investments – short-term profits, long-term growth, hedging against market risk? Your goals will determine the best approach.
- Liquidity: How easily can you exit your position when you want to? Consider the liquidity of the market you’re trading in.
- Regulatory Framework: Are you comfortable with the regulatory environment surrounding the chosen instrument?
Cfd Vs Options
Conclusion
Both CFDs and options offer avenues to participate in the financial markets with potential advantages and drawbacks. CFDs provide a relatively straightforward approach with leverage, while options offer more flexibility and risk management tools. Choosing the right instrument ultimately depends on your individual trading style, knowledge, and risk tolerance. Remember to conduct thorough research, seek professional advice if needed, and always trade responsibly.