Introduction
When trading in foreign exchange (forex), forward options provide investors with a versatile instrument to manage risk, secure a future exchange rate for a currency pair, and potentially capitalize on market volatility. Forward options, often referred to as FX forwards or forward contracts, are derivative contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell a specific amount of a currency at a predetermined exchange rate on a specified future date. Understanding the benefits and mechanics of forward options is essential for forex traders and risk managers seeking to optimize their trading strategies and mitigate currency risk.

Image: www.forexbrokers.com
The Basics of FX Forward Options
A forward option contract specifies the following key elements:
-
Underlying Asset: The currency pair to be exchanged, denoted as the base currency and the counter currency.
-
Notional Amount: The predetermined amount of currency subject to the contract.
-
Exercise Price: The pre-specified exchange rate at which the currency can be bought or sold.
-
Maturity Date: The point in time when the option expires, and the holder has the right to exercise their option.
-
Premium: The upfront payment made by the buyer to the seller for the option to enter or exit the contract in the future.
Types of Forward Options
Forward options can be categorized into two main types:
-
Call Option: Grants the holder the right to buy the base currency against the counter currency at the strike price on the maturity date.
-
Put Option: Grants the holder the right to sell the base currency against the counter currency at the strike price on the maturity date.
Benefits of FX Forward Options
Forward options offer several benefits for forex traders:
-
Hedging Currency Risk: Forward options allow traders to lock in an exchange rate for future currency transactions, protecting against adverse currency fluctuations. This is particularly valuable for importers and exporters seeking to minimize potential losses.
-
Securing Favorable Rates: Forward options enable traders to secure a favorable exchange rate for a future currency transaction. This can be particularly useful when the market exhibits volatility or expectations are for a future change in currency values.
-
Profiting from Volatility: Forward options can also be used to capitalize on market volatility by buying or selling options with different strike prices and maturity dates, creating a synthetic position that seeks to benefit from price fluctuations.
-
Customization: Forward options can be customized to meet specific needs, with flexible strike prices, maturities, and notional amounts.
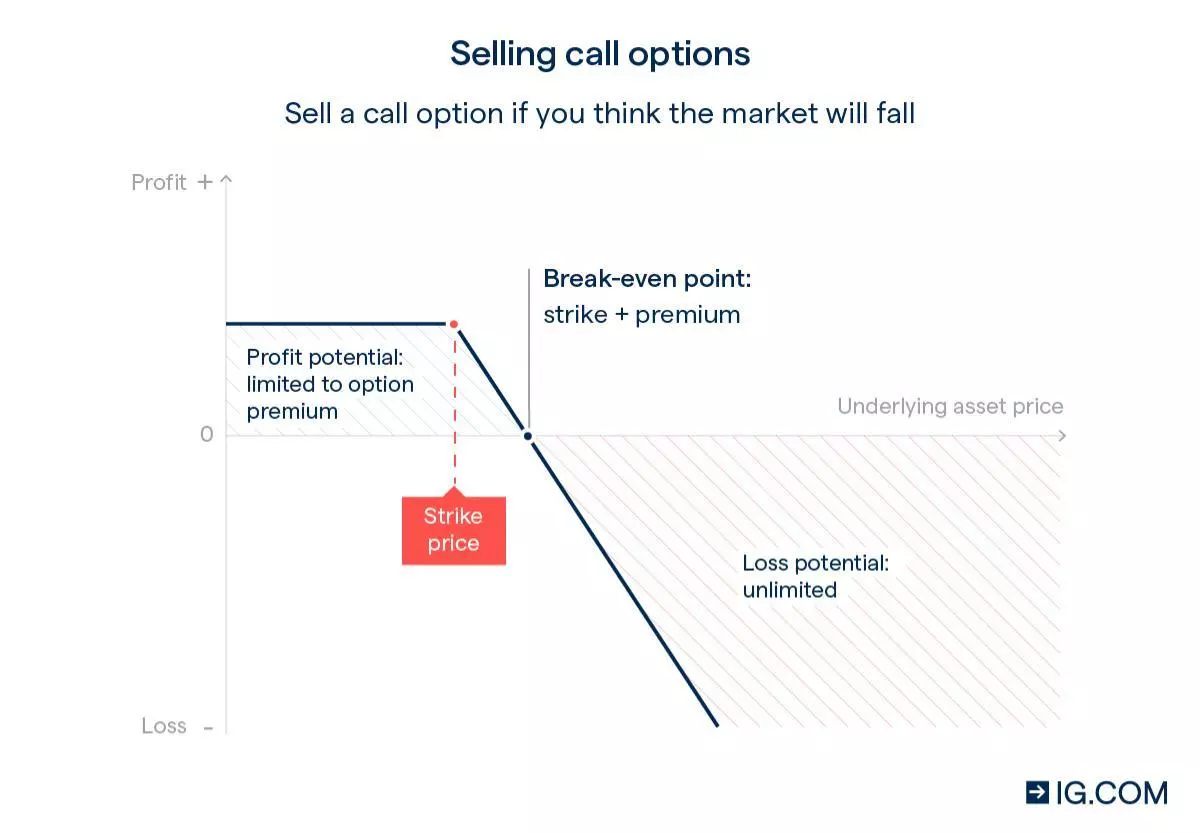
Image: www.ig.com
Trading Forward Options
Trading forward options entails a few key steps:
-
Determine Market Risk and Strategy: Assess the market outlook and define the need for hedging or speculating through forward options.
-
Choose Option Type and Parameter: Select the appropriate option type (call or put) and determine strike price, maturity date, and notional amount.
-
Find a Counterparty: Identify a willing counterparty to the contract, typically a bank, broker, or financial institution.
-
Negotiate Terms: negotiate the premium, exercise price, and other terms of the contract.
-
Execute the Contract: Finalize and execute the forward option contract with the specified terms.
-
Exercise or Close: On the maturity date, the holder has the right to exercise the option or can choose to close the contract for a premium adjustment.
What Is Forward Options In Forex
Conclusion
Forward options provide a powerful tool for managing foreign exchange risk and potentially profiting from currency fluctuations. By understanding the fundamentals, benefits, and trading mechanics of forward options, forex traders and risk managers can develop effective strategies to protect their positions, hedge exposure, and capitalize on market opportunities.






