In the realm of currency trading, understanding the nuances of short positions is paramount to unlocking its potential. A short position, in essence, represents an inverse relationship with a currency pair, where you anticipate a decline in the value of the base currency against the quote currency.
Image: ofpfunding.com
Traders undertake short positions with the expectation of profiting from a depreciation in the base currency. Let’s unravel the complexities of this strategy and equip you with the knowledge to navigate the forex markets like a seasoned pro.
What is a Forex Short Position?
In a short position, you borrow a certain amount of a base currency (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD) and simultaneously sell it in the market, hoping to buy it back later at a lower price. Upon selling the base currency, you acquire an equivalent amount of the quote currency (in this case, USD).
If the value of the base currency falls as you predict, you can repurchase it at a lower price, repay the amount you borrowed, and pocket the difference as profit. To illustrate, suppose you sell 10,000 EUR/USD at 1.1200 and the exchange rate drops to 1.1150. You buy back the 10,000 EUR, repay your borrowed 10,000 EUR, and net a profit of 50 USD.
Advantages of Short Positions
- Profit from Falling Markets: Unlike long positions, short positions allow you to capitalize on market downtrends. This can be particularly valuable in periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical instability.
- Hedging Risk: Traders can employ short positions to mitigate the risks associated with holding long positions. By hedging against potential losses in one currency pair, you can stabilize your overall exposure.
- Leverage Benefits: Forex brokers often provide leverage, enabling traders to control a larger position size than their account balance. This can magnify potential profits, but it’s crucial to manage risk responsibly.
Risks Associated with Short Positions
- Unlimited Loss Potential: Short positions expose traders to potentially unlimited losses if the market moves against them. As the value of the base currency can rise indefinitely, losses can accumulate rapidly.
- Margin Calls: When trading on margin, a trader’s account balance serves as collateral for the borrowed funds. If the market moves significantly against the position, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds or face forced liquidation.
- Borrowing Costs: Depending on the broker and market conditions, traders may incur borrowing costs associated with holding a short position. These costs can erode profits over time.
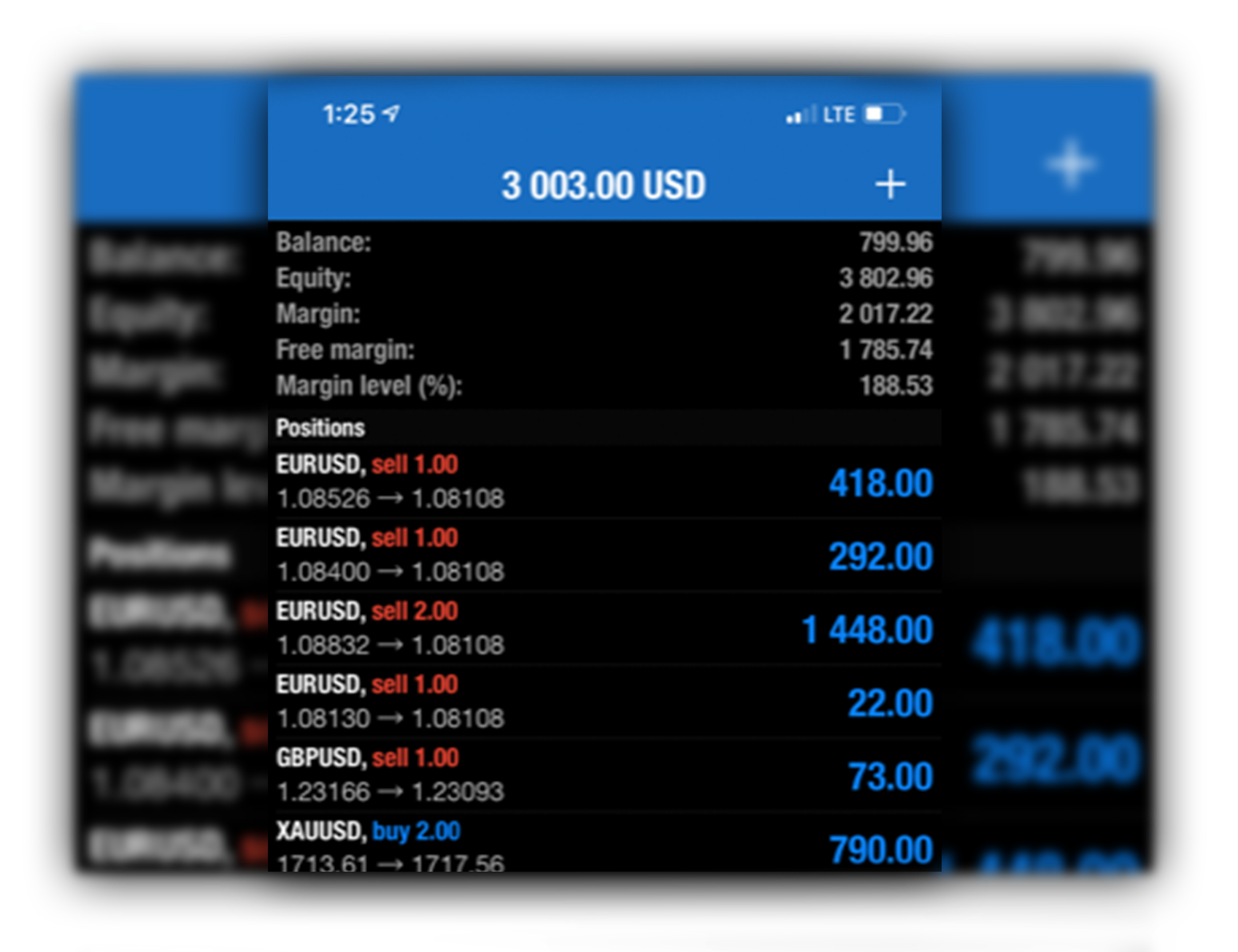
Image: howtotradeonforex.github.io
Factors to Consider Before Shorting
- Market Analysis: Conduct thorough technical and fundamental analysis to assess the fundamental forces influencing the currency pair. Identify potential resistance levels that may indicate a reversal in trend.
- Risk Management: Determine an appropriate position size that aligns with your risk tolerance. Establish clear stop-loss and take-profit orders to mitigate potential losses and lock in profits.
- Trade Psychology: Shorting can amplify emotions as losses can pile up rapidly. Cultivate a disciplined mindset and avoid impulsive trading decisions driven by fear or greed.
What Is Forex Short Position
Conclusion
Mastering the art of short positions in forex trading empowers you to navigate market fluctuations and potentially earn profits. By leveraging these insights and adopting a prudent approach, you can unlock the transformative potential of shorting in the dynamic world of forex. Remember, knowledge and responsible risk management are your faithful companions on this financial adventure.






