Introduction:

Image: theninthworld.com
In today’s globalized economy, the foreign exchange market (Forex) stands as the largest and most liquid financial market, handling trillions of dollars in transactions daily. For individuals and businesses alike, understanding the intricacies of the Forex market is essential for making informed financial decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of Forex through the lens of economists, exploring their insights and analyses to equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this dynamic market effectively.
The Role of Economists in the Forex Market:
Economists play a pivotal role in the Forex market by providing valuable insights and forecasts based on their expertise in economic analysis. They examine economic indicators, such as GDP growth rates, inflation levels, and interest rate policies, to assess the potential impact on currency valuations. By interpreting these indicators, economists can anticipate market trends and guide investors toward informed trading decisions.
Understanding the Forex Market:
Currency Pairs and Currency Values:
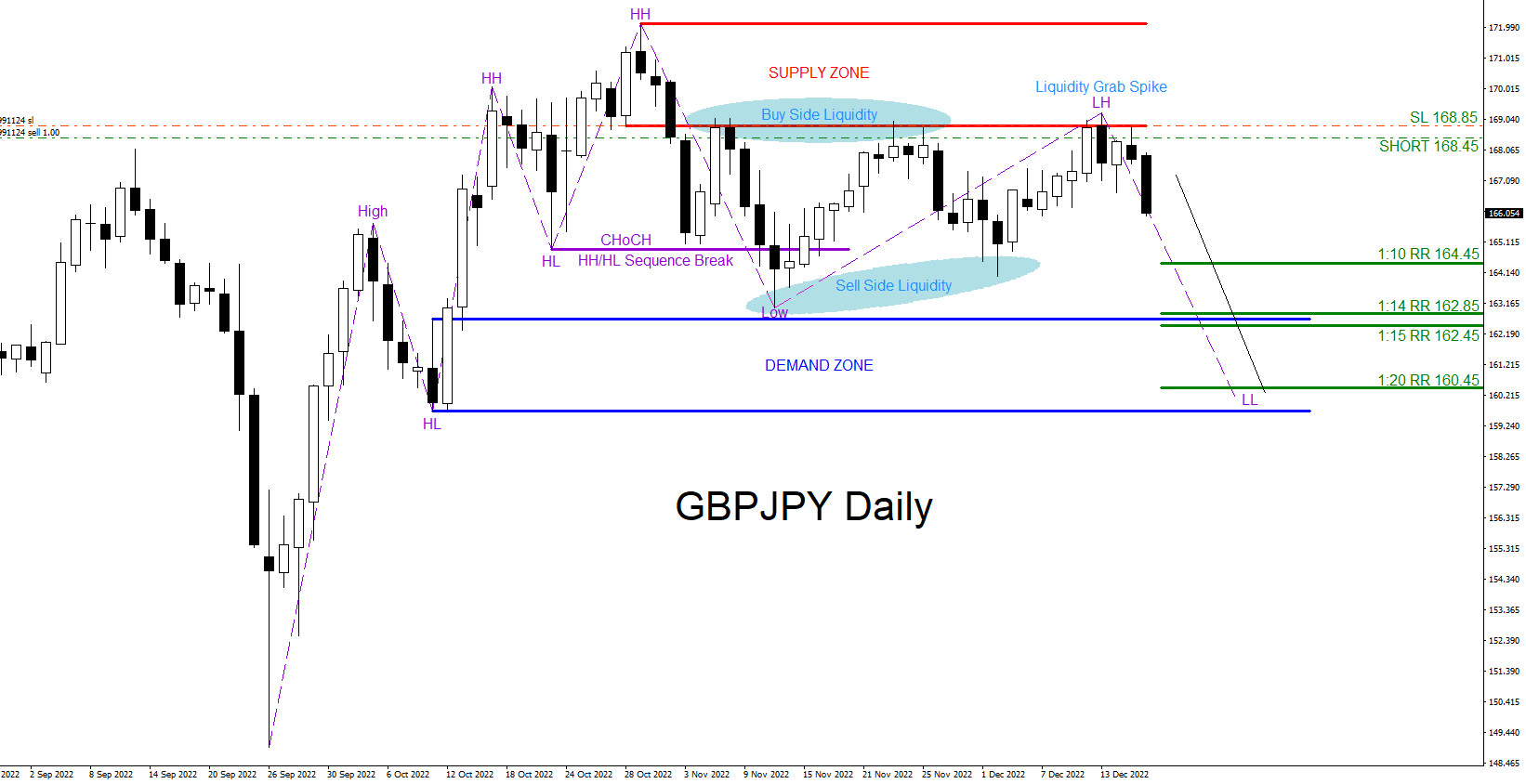
The Forex market revolves around the exchange of currency pairs, representing the value of one currency relative to another. The values of currencies fluctuate continuously in response to various economic factors, including trade imbalances, geopolitical events, and central bank decisions.
Major Currency Pairs:
The Forex market is dominated by a few major currency pairs, including EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar), GBP/USD (British Pound vs. US Dollar), USD/JPY (US Dollar vs. Japanese Yen), and USD/CHF (US Dollar vs. Swiss Franc). These pairs represent a significant portion of Forex transactions and are widely recognized as benchmarks for the global economy.
Historical and Current Trends:
Economists analyze historical price data and current market conditions to identify trends in currency movements. Technical analysis involves studying price charts to identify patterns and predict future price behavior. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, examines economic indicators to assess the underlying factors driving currency valuations.
Factors Influencing Currency Values:
Economic Growth and Stability:
Strong economic growth and stable political conditions typically boost a country’s currency value. High GDP growth rates indicate economic expansion, leading to increased demand for the currency. Political stability fosters investor confidence and attracts foreign investment, further supporting the currency’s strength.
Interest Rates:
Central banks set interest rates to influence economic activity. Higher interest rates attract foreign investors seeking higher returns on their investments, boosting the demand for the domestic currency and increasing its value. Conversely, lower interest rates can weaken the currency by reducing the appeal of domestic investments.
Inflation:
Inflation refers to the increase in the general price level of goods and services. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its value. Central banks aim to control inflation through monetary policy measures, such as adjusting interest rates.
Balance of Payments:
The balance of payments records the value of all transactions between a country and the rest of the world. A trade surplus, where exports exceed imports, strengthens the domestic currency. Conversely, a trade deficit weakens the currency by increasing the demand for foreign currency to pay for imports.
Image: www.finsmes.com
Reviews In Forex Market By Economists
Trading Strategies and Risk Management:
Types of Trading Strategies:
Forex traders employ various strategies to capitalize on currency movements. Scalping involves taking small profits over short intervals based on minute price changes. Swing trading focuses on catching larger price swings over a longer period. Trend following involves riding long-term market trends.
Risk Management:
Managing risk is crucial in Forex trading. Using stop-loss orders and position sizing helps limit potential losses. Moreover, diversifying currency pairs reduces the impact of adverse market movements on a single position.
Economists’ Insights and Market Outlooks:
Leading economists share their perspectives on Forex market trends through market outlooks and forecasts. These insights often consider current economic conditions, upcoming events, and geopolitical risks. By following expert analyses, traders can gain valuable information to inform their trading decisions.
Conclusion:
The Forex market presents both opportunities and challenges for traders. Understanding the complexities of this dynamic market requires a solid foundation in Forex concepts, constant monitoring of economic indicators, and an informed approach to trading. By leveraging the knowledge and insights provided by economists, traders can navigate the Forex market with confidence and make informed decisions to maximize their trading potential.