Understanding Margin in Forex Trading: A Crucial Element
Remember that time I almost lost my shirt in forex trading? I was lured in by the promise of quick profits, and I was overconfident in my trading skills. Little did I know that I was about to experience a devastating margin call. It was a bitter lesson, but one that taught me the importance of understanding margin in forex trading. This crucial element can make or break your trading success, and it’s crucial to grasp it before you even think about placing a single trade.
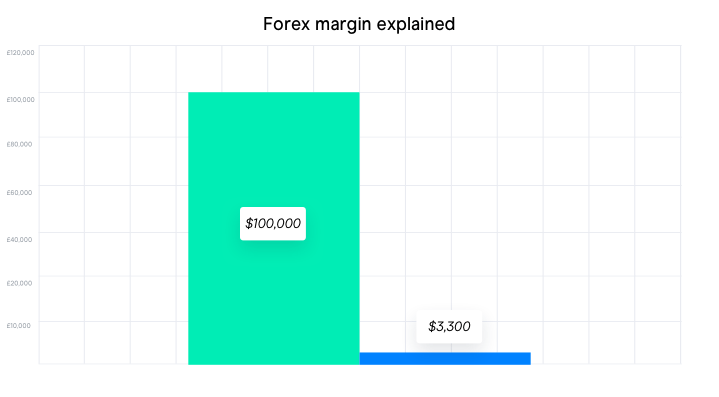
Image: www.cmcmarkets.com
In this detailed guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of margin in forex trading. We’ll explore its definition, purpose, and how it influences your trading strategy. By the end, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how margin works and how to use it effectively. In a nutshell, margin is akin to a security deposit used by brokers to ensure they can cover potential losses arising from your trades.
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
At its core, margin in forex trading is the initial deposit required by your broker to open and maintain a trading position. It serves as collateral, representing a small percentage of the total trade value. Let’s imagine you want to trade 100,000 units of EUR/USD, with a margin requirement of 1%. You would need to deposit $1,000 (1% of $100,000) in your trading account to open this position. This initial deposit acts as a safety net for your broker, protecting them against potential losses in case your trade goes against you.
The Purpose of Margin
Margin plays a vital role in forex trading, providing several fundamental benefits:
- Leverage: Margin allows you to control a larger position with a smaller capital outlay. This leverage can amplify both your profits and losses, making forex trading a high-risk, high-reward endeavor.
- Risk Management: Margin helps in managing your risk by limiting your potential losses. The margin deposit acts as a buffer, preventing you from incurring losses beyond your initial investment.
- Trading Opportunities: Margin enables you to participate in the forex market with limited capital. It opens up more trading opportunities for individuals who might otherwise be restricted by their financial resources.
Margin Requirements and Leverage
Margin requirements are determined by your broker and are influenced by several factors, including the currency pair you’re trading, your account type, and the broker’s risk appetite. The higher the margin requirement, the lower the leverage you have. Conversely, a lower margin requirement provides you with greater leverage, amplifying your potential profits but also your potential losses.
Leverage is essentially the multiplier effect on your trades. A leverage of 1:100, for instance, means that you can control $100 worth of currency with just $1 of your own capital. While leverage can be your greatest ally, it can also be your worst enemy if not managed with caution. It’s imperative to understand the potential risks associated with high leverage and use it responsibly.

Image: forexmacdsystem.blogspot.com
Margin Calls
Here’s where things can get tricky. As a trader, you need to be aware of the potential for margin calls. A margin call occurs when the value of your open position dips below your initial margin deposit. This means your broker requires you to deposit additional funds to maintain the position. A margin call serves as a warning sign that your trade is losing money and could result in liquidation – the forced closure of your position – if you fail to meet the margin call requirement.
Understanding margin calls is essential for managing your risk effectively. Failing to meet a margin call could lead to significant losses, as your position will be closed out at a disadvantageous price. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor your trades closely and set appropriate stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses.
Using Margin Effectively: Tips and Expert Advice
Now, let’s discuss how to use margin effectively and manage your risk wisely:
- Start Small: Begin with a small account balance and gradually increase your trading capital as you gain experience and confidence. This will help you to understand the intricacies of margin and leverage without risking significant losses.
- Limit Leverage: Avoid aggressively utilizing high leverage, especially as a beginner. Start with a lower leverage ratio and gradually increase it as your skills improve. Remember, leverage can magnify both profits and losses.
- Set Realistic Profit Targets: Don’t be overly ambitious with your profit goals. Aim for small and consistent returns, rather than chasing unrealistic gains. This disciplined approach will help you to manage your risk and maintain a long-term perspective.
- Prioritize Risk Management: Always use stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses on every trade. This is crucial for protecting your capital and avoiding catastrophic losses in the event of adverse market movements. You can also employ other risk management strategies, such as trailing stops and position sizing.
Remember, managing margin effectively is about finding a balance between leverage and risk management. By understanding the intricacies of margin and practicing sound risk management principles, you can significantly enhance your trading success and minimize your losses.
FAQ
Q: What happens if I don’t meet a margin call?
A: If you fail to meet a margin call, your broker will liquidate (close) your position to cover the losses. This could result in substantial losses, exceeding your initial margin deposit.
Q: How do I calculate the margin required for a trade?
A: The margin requirement is usually expressed as a percentage of the total trade value. To calculate it, multiply the trade size by the margin percentage. For example, if you want to trade $10,000 worth of EUR/USD and the margin requirement is 1%, you need to deposit $100 ($10,000 x 0.01) in your account.
Q: What are some common margin requirements in forex trading?
A: Margin requirements vary depending on the broker, currency pair, and account type. However, common margin requirements range from 0.5% to 3%.
Q: Can I withdraw my margin funds before closing a trade?
A: No, you cannot withdraw your margin funds until you close your position. The margin serves as collateral for your open trade. Once you close the trade, the margin funds will be returned to your account, minus any trading fees or losses incurred.
What Is Margin In Forex Trading
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tPyMN-7bAZg
Conclusion
In conclusion, margin in forex trading is an essential element that empowers you to control larger positions with limited capital. However, it’s crucial to remember that leverage comes with inherent risks. By understanding the purpose and working principles of margin, using appropriate risk management strategies, and employing expert tips, you can navigate the world of forex trading with greater confidence and minimize your potential losses.
Are you interested in learning more about margin in forex trading? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let’s discuss this critical topic together.