In the realm of international finance, foreign exchange (forex) trading plays a pivotal role. And when it comes to the bustling streets of India, foreign exchange traders and investors must navigate the intricacies of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. Understanding the nuances of CGST and SGST for forex transactions empowers financial professionals and enthusiasts alike to make informed decisions.
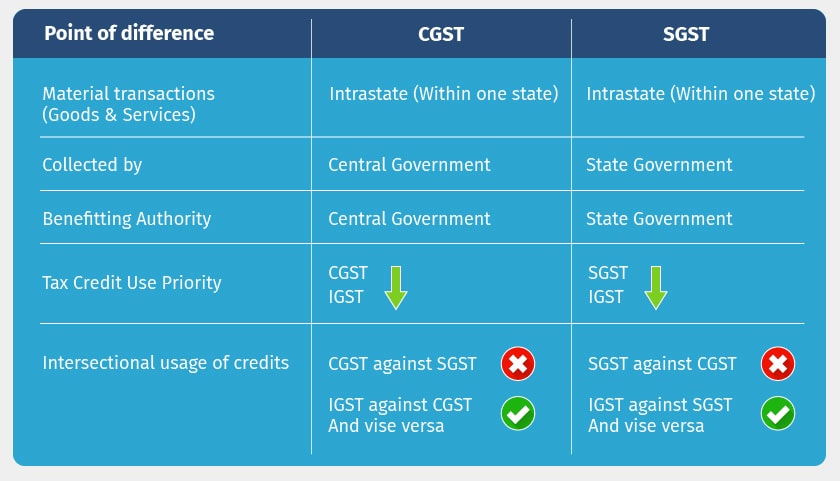
Image: tallysolutions.com
Dive into the intricacies of the Indian GST system, unraveling the complexities of CGST and SGST as they pertain to forex trading, and equip yourselves with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) and State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
The Indian GST system is a dual tax structure, encompassing both CGST and SGST. When it comes to forex transactions, the following rules apply:
- Inter-state transactions: CGST and SGST are levied at 50% each.
- Intra-state transactions: Only SGST is applicable.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for determining the applicable tax rates and filing obligations.
Implications for Forex Transactions
Forex trading is considered a taxable service under the GST regime. This means that any forex dealer or broker is liable to pay GST on the services rendered. The GST rate for forex trading is currently set at 18%, which includes both CGST and SGST of 9% each. Forex traders are required to register for GST and file regular returns, ensuring compliance with the tax laws.
Furthermore, forex brokers are obligated to collect GST from their clients on any brokerage charges or fees. The collected GST must be deposited to the government treasury, adhering to prescribed deadlines and procedures.
Key Trends and Developments
The GST regime for forex trading has undergone several changes in recent years, keeping pace with evolving market dynamics. Notable updates include:
- GST rate reduction: In 2021, the GST rate for forex trading was reduced from 18% to 5%, providing relief to traders and investors.
- Advance Ruling Authority (ARA) interventions: The ARA has clarified specific GST-related issues pertaining to forex trading, offering guidance on matters such as classification of services and treatment of foreign currencies.
Stay abreast of the latest updates and developments to ensure compliance and leverage opportunities.
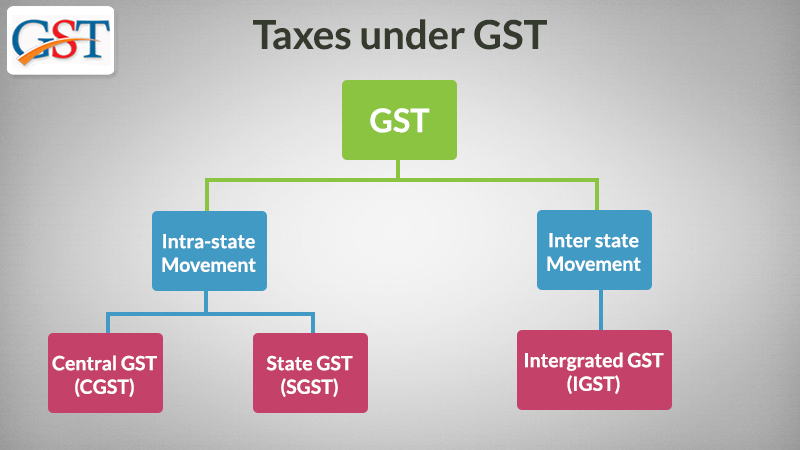
Image: malayhaidir.blogspot.com
Expert Advice and Tips
Navigating the forex GST landscape can be complex. Here are some practical tips to simplify the process:
- Seek professional guidance: Consult with a chartered accountant or tax advisor who specializes in GST to gain clarity and ensure compliance.
- Maintain meticulous records: Keep accurate and detailed records of all forex transactions, including invoices and receipts, for GST filing purposes.
By incorporating these tips into your forex trading strategy, you can enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and mitigate potential risks.
FAQs on Forex GST
To further clarify the topic, here are some commonly asked questions and their concise answers:
- Who is liable to pay GST on forex transactions?
- What is the current GST rate for forex trading?
- Are there any exemptions or concessions available under the forex GST regime?
All individuals and entities registered as forex dealers or brokers are responsible for paying GST on their forex-related services.
The GST rate for forex trading in India is currently 18%, consisting of 9% CGST and 9% SGST.
There are no specific exemptions or concessions for forex trading under the GST framework.
Cgst And Sgst On Forex
Conclusion
Navigating CGST and SGST for forex trading in India requires a deep understanding of the GST regime. By grasping the fundamental concepts, keeping abreast of the latest trends, and adhering to the prescribed guidelines, you can ensure compliance, optimize your forex trading activities, and seize opportunities in this dynamic financial landscape.
If you have found this article informative and valuable, please consider sharing it with your peers and subscribing to our blog for regular updates on GST and its implications for various sectors. Let’s continue exploring the world of taxation together!






