Introduction
In the realm of international finance, foreign exchange reserves play a pivotal role in maintaining economic stability and supporting economic growth. India, being a rapidly developing nation, is no exception to this rule. This article delves into the history of India’s forex reserves, with particular emphasis on the significant events in 1991 that shaped the trajectory of India’s economic fortunes.
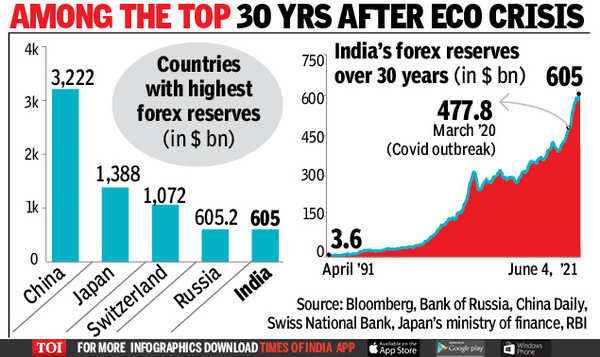
Image: currentaffairs.adda247.com
Foreign Exchange Reserves: A Primer
Foreign exchange reserves refer to the stock of financial assets held by a country’s central bank in various international currencies and other liquid assets. These reserves serve as a cushion against external economic shocks, such as fluctuations in exchange rates or disruptions in trade. The composition of forex reserves includes currencies like US dollars, euros, Japanese yen, and British pounds, as well as gold and other reserve assets.
India’s Forex Reserves Crisis of 1991
In 1991, India faced a severe foreign exchange crisis. The country’s forex reserves had dwindled to a mere $1.8 billion, barely enough to finance three weeks of imports. This crisis stemmed from a confluence of factors, including global economic headwinds, political instability, and the impact of the 1990 Gulf War, which had caused a sharp increase in oil import costs.
The crisis threatened to cripple India’s economy. Without adequate foreign currency, the country would find it difficult to pay for essential imports, such as oil, fertilizers, and raw materials. The value of the rupee plunged, leading to inflationary pressures and a loss of confidence among international investors.
Economic Reforms and Structural Adjustments
In the face of this crisis, the Indian government embarked on a series of bold economic reforms and structural adjustments. These measures were designed to reduce government spending, liberalize trade, and promote foreign direct investment.
The government devalued the rupee in two tranches, making exports more competitive and discouraging imports. Interest rates were hiked to curb inflation and attract foreign capital. The government also introduced a new foreign investment policy, permitting foreign companies to enter various sectors of the Indian economy.

Image: currentaffairs.adda247.com
Benefits of the Economic Reforms
The economic reforms of 1991 had a profound impact on India’s forex reserves. Foreign direct investment surged, boosting the country’s foreign exchange reserves. The liberalization of trade led to an increase in exports and a reduction in imports. The devaluation of the rupee made Indian products more competitive in the global market.
Over time, India’s forex reserves steadily increased. This growth was driven by strong economic growth, a surge in foreign direct investment, and prudent management of external debt. By 2023, India’s forex reserves had crossed $600 billion, a remarkable turnaround from the crisis of 1991.
India Forex Reserves In 1991
Conclusion
The foreign exchange reserves of India have come a long way since the crisis of 1991. The economic reforms and structural adjustments implemented during that period laid the foundation for a more robust and resilient economy. Today, India’s forex reserves provide a strong cushion against external economic shocks and support the ongoing economic growth of the country.






