Introduction
In the realm of finance, leverage plays a pivotal role in magnifying returns. However, it also amplifies risks, making it essential for traders to understand the concept of maintenance margin — a crucial safeguard that helps navigate the complexities of margin trading.
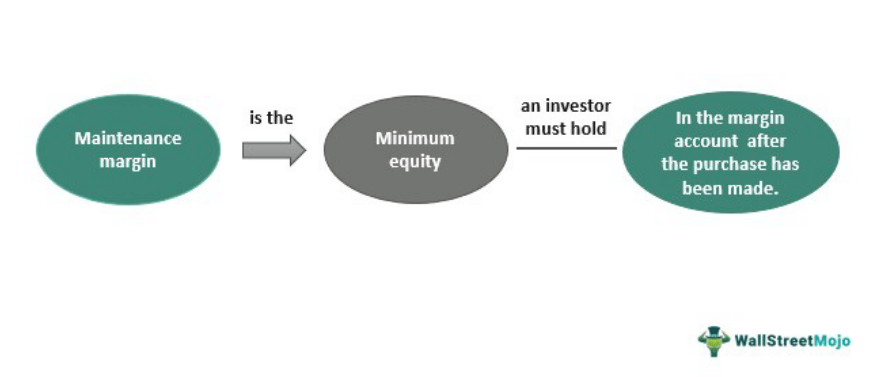
Image: www.wallstreetmojo.com
This article will delve deep into the maintenance margin equation, exploring its significance, calculation, and implications. By unlocking the secrets of this equation, traders can employ leverage effectively while controlling risks and maximizing their trading potential.
Understanding Maintenance Margin
Maintenance margin is the minimum equity that must be maintained in a margin account to prevent it from falling below the threshold set by the brokerage firm. It represents the buffer that protects against losses that could cause a margin call, where the trader would be required to deposit additional funds or liquidate positions to fulfill margin requirements.
The maintenance margin level varies among different brokerages and can range from 25% to 50% or more. This level is established to manage risk and ensure that traders have sufficient equity to absorb fluctuations in the value of their positions without facing margin calls.
Calculating Maintenance Margin
The maintenance margin is calculated as a percentage of the initial margin, which is the amount of equity required to open a margin position. The initial margin is typically expressed as a percentage of the position’s total value. For example, if a trader opens a position worth $10,000 with an initial margin requirement of 50%, they would need to deposit $5,000.
The maintenance margin is then calculated as a percentage of the initial margin. For example, if the maintenance margin level is set at 30%, the trader would need to maintain an equity balance of at least 30% of the initial margin, or $1,500 in this case.
Implications for Margin Trading
The maintenance margin equation has profound implications for traders who employ leverage in their strategies. Here are some key considerations:
- Risk Management: Maintenance margin acts as a risk management tool, preventing traders from overleveraging their accounts and potentially facing margin calls. By maintaining sufficient equity, traders can withstand market downturns without being forced to liquidate positions prematurely.
- Account Stability: By preserving sufficient equity above the maintenance margin level, traders create a buffer against adverse market movements that could erode their account balance. This helps maintain account stability and provides traders with more flexibility to respond to market changes.
- Margin Call Avoidance: Traders who fall below the maintenance margin level trigger a margin call, requiring them to deposit additional funds or liquidate positions to bring their account back above the threshold. By monitoring equity levels and ensuring they meet maintenance margin requirements, traders can avoid costly margin calls.
- Trading Capacity: Maintenance margin also impacts the trading capacity of an account. The higher the maintenance margin level, the less leverage traders can employ. This can limit trading opportunities and potential returns for traders seeking to maximize leverage.

Image: www.sbnewsroom.com
Maintenance Margin Equation
Conclusion
The maintenance margin equation is a fundamental concept in margin trading that empowers traders to navigate the risks and rewards associated with leverage effectively. By understanding the calculation and implications of maintenance margin, traders can establish sound risk management strategies, preserve account stability, and avoid margin calls. As with any leveraged trading strategy, it is crucial to exercise prudence and thoroughly assess risk tolerance before incorporating leverage into trading practices.
By leveraging the principles outlined in this article, traders can harness the power of maintenance margin to elevate their trading strategies, optimize risk management, and pursue informed investment decisions.