In the labyrinthine world of financial markets, understanding the nuances between various trading instruments is paramount. Among the most frequently encountered are CFDs (Contracts for Difference) and Forex (Foreign Exchange). While both offer opportunities for potential profits, their inherent characteristics and intricacies set them apart. Embark on an intellectual odyssey as we delve into the enigmatic realm of CFDs and Forex, unraveling their captivating distinctions.

Image: www.cfdspy.com
CFDs, or Contracts for Difference, are derivative financial instruments that emulate the price action of an underlying asset. Unlike traditional ownership, CFDs grant traders speculative exposure to the price fluctuations of the underlying asset without actual ownership. This financial instrument has gained immense popularity due to its multifaceted nature, allowing traders to speculate on both rising and falling markets. Moreover, CFDs provide unparalleled flexibility, as they can track a vast array of underlying assets, encompassing stocks, commodities, indices, and even cryptocurrencies.
In stark contrast, Forex, or Foreign Exchange, represents the global marketplace for the exchange of currencies. It serves as a decentralized network of banks, brokers, and individuals, facilitating the conversion of currencies for commercial transactions or investment purposes. Unlike CFDs, Forex trading involves the actual exchange of physical currencies, where traders profit from disparities in currency values. The Forex market is renowned for its vast liquidity, making it highly accessible and conducive to active trading.
Deciphering the Fundamental Distinctions
To fully grasp the intrinsic differences between CFDs and Forex, it is imperative to scrutinize their fundamental attributes.
-
Underlying Asset
CFDs are essentially agreements between two parties, whereby the seller agrees to pay the buyer the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and its price at the expiration date. The underlying asset can be any financial instrument, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or even cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, Forex involves the actual exchange of fiat currencies, such as USD, EUR, or GBP, eliminating the presence of an underlying asset.
-
Ownership
CFD trading does not entail ownership of the underlying asset. Traders merely speculate on the price movements, profiting or losing based on the accuracy of their predictions. Conversely, Forex trading involves the actual ownership and exchange of one currency for another, with the aim of capturing discrepancies in exchange rates.
-
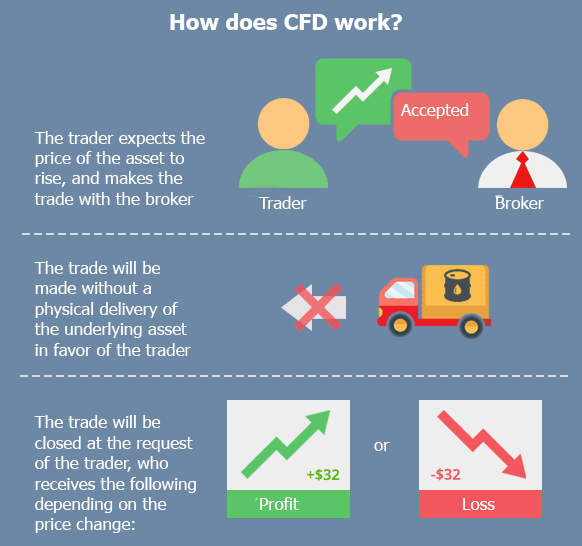
Image: fxssi.comLeverage
Leverage is a double-edged sword that can amplify both profits and losses. CFDs frequently offer higher leverage ratios compared to Forex, enabling traders to control a larger position size with a smaller initial investment. However, it is crucial to employ leverage judiciously, as it can exacerbate losses if the market moves adversely.
-
Settlement
CFDs are typically settled in cash, with no physical delivery of the underlying asset. This characteristic enhances flexibility and expedites trade execution. Forex transactions, on the other hand, involve the actual exchange of currencies, necessitating settlement through designated platforms or brokers.
Difference Between Cfd And Forex
Harnessing the Power of CFDs and Forex
Both CFDs and Forex offer distinct advantages, catering to diverse trading preferences and objectives.
CFDs:
-
Unparalleled Flexibility: CFDs empower traders to speculate on a wide spectrum of underlying assets, including those that may not be immediately accessible through direct ownership.
-
Magnified Profits: The judicious use of leverage can amplify profits, potentially resulting in substantial returns on investment.
-
Hedging Opportunities: CFDs can be employed as hedging instruments to mitigate risks associated with existing investments.
Forex:
-
Liquidity: The Forex market is known for its exceptional liquidity, making it highly accessible and responsive to changing market conditions.
-
Transparency: Forex transactions are generally transparent, with real-time data readily available to traders, facilitating informed decision-making.
-
Accessibility: Forex trading is relatively accessible, with minimal entry barriers and a multitude of brokers offering trading services.






