Imagine a colossal marketplace, a swirling vortex of financial transactions so vast that it dwarfs the GDP of most countries. This is the domain of the foreign exchange market (forex), where currencies dance to the dictates of global economies and investors seek fortunes. Every business day, an eye-popping amount of money circulates through this relentless financial bloodstream, fueling economic growth and shaping the very fabric of global economies.
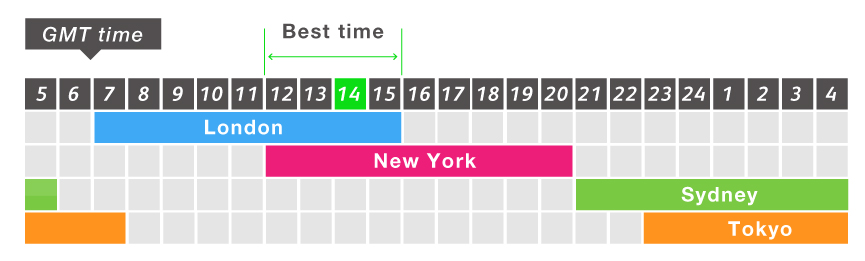
Image: tradingsitus.blogspot.com
The daily turnover in the forex market is a staggering testament to its significance in the modern financial landscape. According to the latest figures from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), over USD 6.6 trillion worth of currencies were traded daily in April 2022. That’s more than six times the entire global trade in goods and services!
Unveiling the Anatomy of the Forex Market
This colossal turnover is facilitated by a multitude of market participants, including banks, investment firms, corporations, hedge funds, and individual traders. These actors engage in buying and selling currencies to facilitate international trade, hedge against currency fluctuations, or simply speculate on market movements.
The forex market operates 24/5, with trading occurring round the clock in different time zones. The market’s participants are spread across the globe, creating a truly globalized ecosystem where currencies are exchanged seamlessly, irrespective of geographic boundaries.
The Interplay of Supply and Demand
The dance of currencies in the forex market is driven by the fundamental principles of supply and demand. When demand for a particular currency exceeds supply, its value rises. Conversely, if supply outweighs demand, the currency’s value falls.
Several factors influence supply and demand in the forex market. These include global economic conditions, interest rate differentials, political stability, and geopolitical events. Traders constantly monitor these factors, seeking to anticipate market movements and capitalize on opportunities.
The Currency Pair System
In the forex market, currencies are not traded in isolation but rather in pairs. The most commonly traded pair is the EUR/USD, representing the exchange rate between the euro and the US dollar. Other popular pairs include the USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and EUR/JPY.
When you trade a currency pair, you are essentially buying one currency while simultaneously selling the other. Your profit or loss depends on the direction of the exchange rate movement. For instance, if you buy EUR/USD and the euro appreciates against the dollar, you will profit.

Image: www.youtube.com
The Power of Leverage
One of the distinctive features of the forex market is the use of leverage. Leverage allows traders to control larger amounts of capital than they actually possess. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses.
Traders must exercise caution when using leverage, as excessive leverage can lead to significant financial losses. Proper risk management practices are essential to mitigate the risks associated with leveraged trading.
The Impact of the Forex Market
The forex market plays a pivotal role in the global economy. It provides businesses with the means to manage risks associated with international trade. It enables investors to diversify their portfolios and speculate on currency movements.
The forex market also serves as a barometer of global economic health. Currency exchange rates reflect the perceived strength of different economies, providing insights into global trade flows, economic growth, and political stability.
How Much Money Is Traded Daily On Forex
Conclusion
The foreign exchange market is a colossal, ever-moving tide that shapes the global financial landscape. Its daily turnover of trillions of dollars underscores its significance in facilitating global trade, hedging against currency risks, and providing investment opportunities. As the world’s economies become increasingly interconnected, the forex market will continue to play a vital role, shaping the course of global commerce and influencing the very fabric of our financial system.






