Navigating the dynamic forex market requires savvy tools to make informed trading decisions. Among the most effective technical indicators, moving averages hold a special place in the traders’ arsenal. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the types of moving averages, their significance, and how to utilize them strategically for successful forex trading.
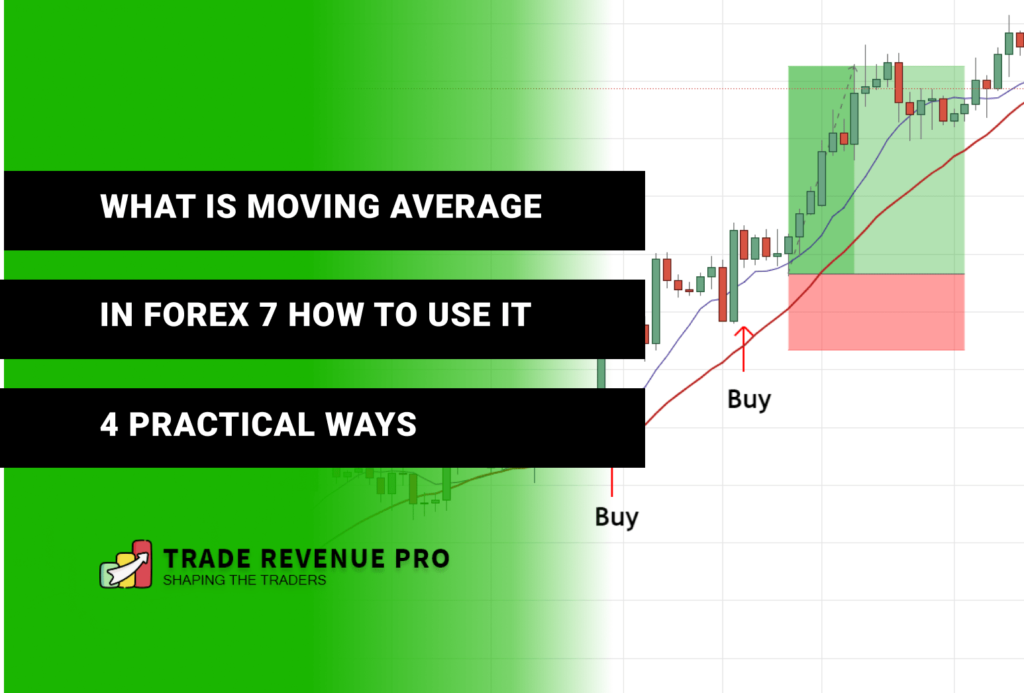
Image: traderevenuepro.com
Understanding Moving Averages
A moving average (MA) is a widely used technical analysis tool that calculates the average price of a security over a specific period. It helps traders identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential trading opportunities. By smoothing out price fluctuations, moving averages provide a clearer picture of the market’s overall direction, eliminating market noise.
Types of Moving Averages
The forex market employs various types of moving averages, each tailored to specific trading styles and timeframes. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculated by summing the closing prices over a specific period and dividing by the number of periods. The SMA is the most straightforward and widely used type of moving average.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Places greater weight on recent prices, giving more importance to the latest market movements. The EMA responds more quickly to price changes than the SMA.
- Smoothed Moving Average (SMMA): Combines a simple moving average with an exponential moving average, resulting in a smoother and less volatile indicator than the EMA.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA): Assigns different weights to prices over a specific period, with more emphasis on recent prices. The WMA responds more sensitively to price changes than the SMA.
- Hollow Indicator: Calculates the difference between two moving averages, highlighting possible trading opportunities.
Benefits of Using Moving Averages
Moving averages offer numerous benefits to forex traders:
- Trend Identification: Moving averages can help identify the prevailing trend in the market. An upward sloping MA suggests an uptrend, while a downward sloping MA indicates a downtrend.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Moving averages can act as support and resistance levels, as prices tend to test and bounce off these indicators.
- Trading Signals: Crossovers between different moving averages can generate trading signals, indicating potential trend changes or continuation.
- Confirmation: Moving averages can be used to confirm price patterns or other technical indicators, providing greater confidence in trade decisions.

Image: www.dolphintrader.com
Applications of Moving Averages
Moving averages find wide application in forex trading strategies:
- Trend Following: Traders can use moving averages to identify and follow trends, entering trades in the direction of the trend.
- Range Trading: Moving averages can help identify trading ranges, allowing traders to capitalize on price fluctuations within a defined price zone.
- Counter-Trend Trading: Some traders use moving averages to identify potential reversals and trade against the prevailing trend.
- Scalping: Short-term traders (scalpers) rely on moving averages to pinpoint trading opportunities within small price movements.
Choosing the Right Moving Average
Selecting the appropriate moving average depends on the trader’s trading style and timeframe:
- Short-Term Trading: EMAs or hollow indicators are suitable for short-term trading as they respond quickly to price changes.
- Medium-Term Trading: SMAs or WMAs with periods between 20 and 50 are commonly used for medium-term trading strategies.
- Long-Term Trading: Long-term traders may employ SMAs with periods of 100 or more to identify major trends and market cycles.
Types Of Moving Average In Forex
Conclusion
Moving averages are indispensable tools in the forex trader’s toolbox. By understanding the different types of moving averages and their applications, traders can enhance their technical analysis skills, identify potential trading opportunities, and make informed decisions in the dynamic forex market. Remember, mastering the art of moving averages requires practice and a thorough understanding of the underlying market dynamics.






