In the bustling realm of home improvement, Home Depot stands as a colossal force, its impact reverberating throughout neighborhoods and commercial spaces alike. As investors navigate the dynamic world of stocks, understanding Home Depot’s price-to-earnings (PE) ratio is indispensable, a key metric that unlocks insights into its financial health and future prospects. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of Home Depot’s PE ratio, exploring its significance, revealing its implications, and empowering you to make informed decisions.

Image: www.sec.gov
Deciphering the Price-to-Earnings Ratio: A Gateway to Understanding
The price-to-earnings ratio, often referred to as the PE ratio, stands as a fundamental indicator in the financial world. It provides a snapshot of how the market values a company’s earnings, offering a yardstick to gauge its attractiveness relative to peers. To calculate the PE ratio, one simply divides the current market price of a share by its annual earnings per share.
Comprehending the PE ratio is pivotal for investors seeking to assess a company’s valuation. A high PE ratio suggests that investors are willing to pay a premium for each dollar of earnings, indicating optimism about the company’s growth potential. Conversely, a low PE ratio may signal that the market undervaluing the company’s earnings, potentially presenting an investment opportunity.
Home Depot’s PE Ratio: A Reflection of its Market Standing
Home Depot’s PE ratio has consistently hovered around the 20 to 25 range in recent years, indicating that investors generally perceive it as a stable and profitable company with solid growth prospects. This valuation reflects Home Depot’s position as a leading home improvement retailer, benefiting from a vast network of stores, a loyal customer base, and a strong brand reputation.
However, it’s essential to recognize that the PE ratio is not static and can fluctuate based on various factors, including economic conditions, industry trends, and company-specific developments. Understanding these dynamics is key to interpreting Home Depot’s PE ratio and making informed investment decisions.
Navigating Home Depot’s PE Ratio: A Guide for Investors
When evaluating Home Depot’s PE ratio, it’s crucial to consider the following aspects:
-
Industry Comparison: Comparing Home Depot’s PE ratio to that of its peers in the home improvement sector provides a valuable context. If Home Depot’s PE ratio is significantly higher or lower than its competitors, it may warrant further investigation into the underlying reasons.
-
Historical Trends: Analyzing Home Depot’s PE ratio over time can reveal patterns and trends. Consistent PE ratios indicate stability, while significant fluctuations may signal changes in market sentiment or company performance.
-
Growth Prospects: The PE ratio incorporates market expectations for future growth. A high PE ratio implies that investors anticipate robust earnings growth, while a low PE ratio may indicate more modest growth expectations.
-
Economic Conditions: Broader economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and consumer confidence, can impact Home Depot’s PE ratio. Understanding the macroeconomic landscape is crucial for assessing the company’s valuation.
-
Company-Specific Factors: News and events specific to Home Depot, such as new store openings, product launches, or management changes, can also influence its PE ratio. Staying abreast of company-specific developments is essential for accurate interpretation.
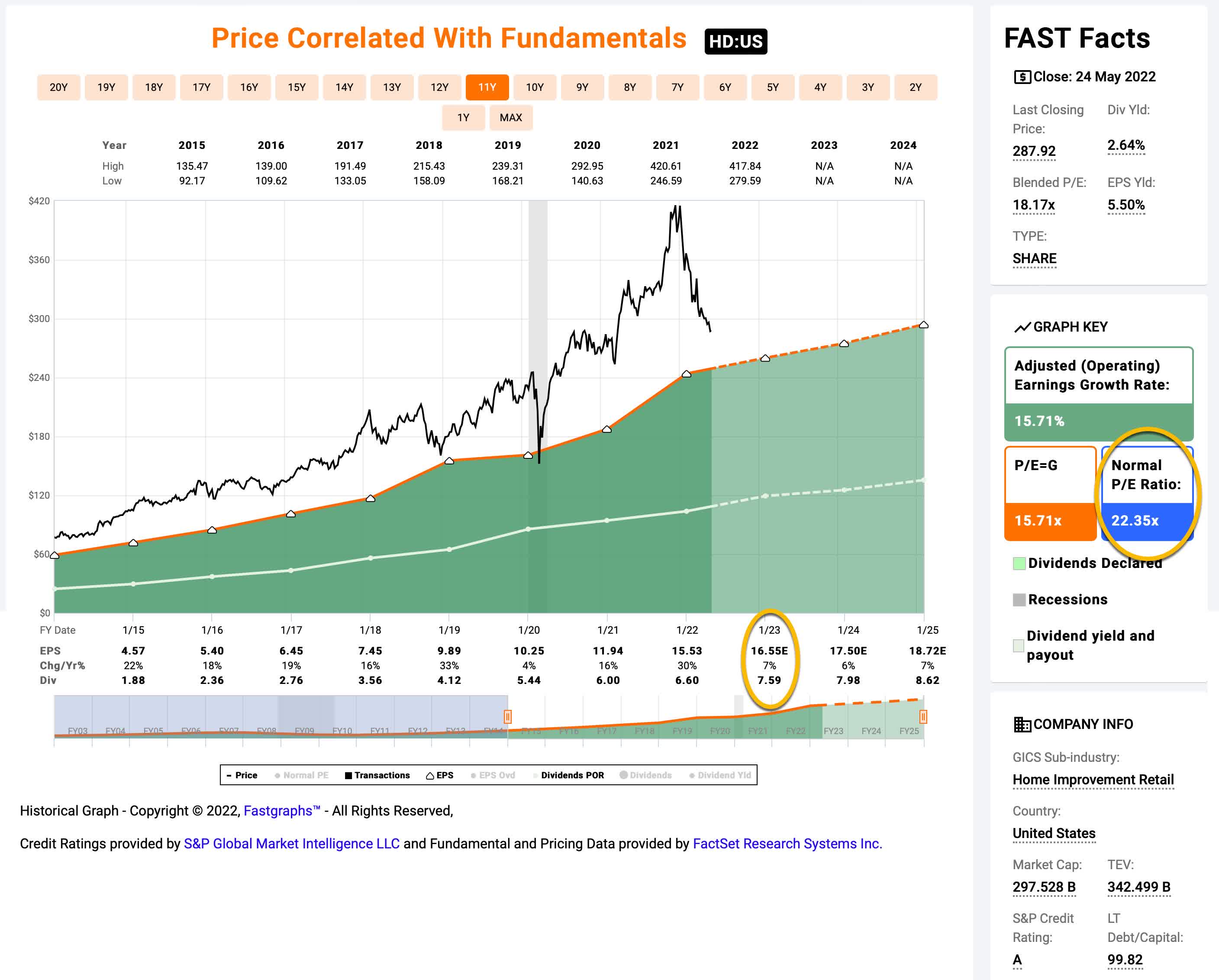
Image: seekingalpha.com
Home Depot Pe Ratio
Beyond the PE Ratio: A Holistic Approach to Investment
While the PE ratio is a valuable metric, it’s crucial to recognize that it’s just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to evaluating a company’s investment potential. Other